~ |
Online free nautical charts and publications
open data/open access - libre accès
Cartes marines gratuites et ouvrages nautiques en ligne
 | V |



| COM | 
| ||
International organizations/ Organisations internationales
Cospas‑Sarsat EAHC IALA IHO IMO ITU NSC WMO
About Nautical Free
Nautical Free provides a list of free nautical charts and online publications.There is a list by country from letter A to letter V, for each country the organizations and for each organization a list of free online documents (charts, nautical books, notice to mariners...). There is two special lists: one for the international organizations and one for the private companies. There is also a reverse list by type of documents: sailing directions, radio signals, tide tables, nautical charts... You can also find on Nautical Free wave forecast maps for tomorrow, space weather forecast for GPS, how to check your computer clock, as well as information about celestial navigation or about ice navigation...
Au sujet de Nautical Free
Nautical Free fournit une liste de cartes marines gratuites et d'ouvrages nautiques en ligne.Il y a une liste par pays de la lettre A à la lettre V, pour chaque pays les organisations et pour chaque organisation une liste de documents libres en ligne (cartes marines, ouvrages nautiques, avis aux navigateurs...). Il existe deux listes spéciales : une pour les organisations internationales et une pour les sociétés privées. Il existe également une liste inverse par type de documents : instructions nautiques, ouvrages de radiosignaux, tables des marées, cartes marines... Vous trouverez également sur Nautical Free des cartes de prévision de la hauteur des vagues pour demain, des prévisions de la météo de l'espace pour les GPS, comment vérifier l'heure de son ordinateur, ainsi que des informations sur la navigation astronomique ou la navigation dans les glaces...
Advice / Conseils
For navigation use only updated regulatory documents /
Pour la navigation n'utiliser que des documents réglementaires à jour.
GPS is more accurate than nautical charts /
Un GPS est plus précis qu'un carte marine
Web Servers / Serveurs Web
You can use the nearest or faster server / Vous pouvez utiliser le serveur le plus proche ou le plus rapide :
- French mirror with one page by section / Serveur en France avec une page par section : http://nauticalfree.free.fr
- French mirror on one page / Serveur en France sur une page : http://nauticalfree.free.fr/onepage.html
- French mirror without image on one page / Serveur en France sans image sur une page : http://nauticalfree.free.fr/noimage/
- US mirror with one page by section / Serveur au États-Unis avec une page par section : http://nauticalfree.eu5.org
- US mirror on one page / Serveur au États-Unis sur une page : http://nauticalfree.eu5.org/onepage.html
- US mirror without image on one page / Serveur au États-Unis sans image sur une page : http://nauticalfree.eu5.org/noimage/
- US mirror on seven pages / Serveur au États-Unis sur sept pages : https://sites.google.com/site/nauticalfree/
Caption / Légende
- The nautical books are in standard fonts / Les ouvrages sont en caractères droits
- In Italic the maps and the charts / Les cartes sont en italiques
- The last item for an organization is the Notices to Mariners. The first issue of each year is often a special publication /
La dernier item pour un service hydrographique est un lien vers les avis au navigateurs. Le premier numéro de chaque année est souvent un numéro spécial
- Raster Navigational Charts (RNC)
- Bitmap electronic images of paper charts that conform to IHO standard S-61 /
Carte marine matricielle, fac-similé numérique d'une carte papier (scan) conforme à la norme de l'OHI S-61 - Electronic Navigational Charts (ENC)
- Vector charts that conform to IHO standard S-57 /
Carte électronique de navigation, carte vectorielle conforme à la norme de l'OHI S-57
|
|
Cartes marines gratuites et ouvrages nautiques en ligne : Organisations internationales
International organizations / Organisations internationales
- Cospas-Sarsat: Satellite System for Search and Rescue
- East Asia Hydrographic Commission (EAHC)
- International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA)
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO)
- Organisation Hydrographique Internationale (OHI)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Union internationale des télécommunications (UIT)
- NATO Shipping Centre (NSC)
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
Cospas-Sarsat: Satellite System for Search and Rescue
- Cospas-Sarsat system overview
The basic Cospas-Sarsat concept for search and rescue: Distress radiobeacons (406MHz), LEOSAR, GEOSAR, MEOSAR, Local User Terminals (LUTs), Mission Control Centres (MCCs).
- Introduction to the Cospas-Sarsat system
This document introduces potential users to the Cospas-Sarsat System: a satellite-based beacon alert communication system for the support of Search and Rescue (SAR) operations around the world. The System uses spacecraft and ground facilities to detect and locate distress signals from emergency beacons carried on boats, on aircraft, and by individuals. The distress alert information, including the position of the distress beacon and other related information (such as the information provided when the beacon was registered), is sent by Cospas-Sarsat to the appropriate SAR authorities. Distress beacons include Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs, for use on aircraft), Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBs, for use on ships), and Personal Locator Beacons (PLBs, for use in multiple environments by individuals).
- Transition to MEOSAR
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme initiated the development of the Medium-altitude Earth Orbiting Satellite System for Search and Rescue (MEOSAR system), with SAR repeaters placed on the satellites of the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) of Europe (Galileo), Russia (Glonass) and the USA (GPS). MEOSAR complements the existing LEOSAR (satellites in low-altitude orbits) and GEOSAR (satellites in geostationary orbit) systems, and will eventually replace the LEOSAR system.
- Cospas-Sarsat Beacon FAQ
A Cospas-Sarsat beacon, also called a distress radio beacon or emergency beacon, is a radio transmitter that can be activated in a life-threatening emergency to summon assistance from government authorities. When a distress beacon is activated, it transmits a signal at 406 MHz that can be detected by satellites. As the satellites orbit the earth, they "listen" for any activated beacons and carry the beacon signals to ground stations that compute their positions and report to rescue authorities. A beacon for use aboard a marine vessel is called an Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB). Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about distress beacons, Registration and Troubleshooting.
- Handbook on Distress Alert Messages
The purpose of this document is to provide Rescue Coordination Centre (RCC) personnel and Search and Rescue Point of Contact (SPOC) personnel with an overview of the Cospas-Sarsat System and an understanding of the Cospas-Sarsat distress alert messagesand their contents. This will allow RCCs and SPOCs to manage the response to search and rescue (SAR) incidents involving Cospas-Sarsat distress alerts in an informed manner.
- Handbook of Beacon Regulations
This document provides a summary of regulations issued by Cospas-Sarsat Participants regarding the carriage of 406 MHz beacons. This document is based mainly on information provided by Participants at Cospas-Sarsat meetings and in reports on System status and operations. Some information was provided by non-Cospas-Sarsat Participants. However, regulations are likely to evolve and the attached information should not be regarded as an official record of their current status.
- Cospas-Sarsat Glossary: English, French & Russian
The purpose of this document is to provide an alphabetical list of specialized terms and acronyms relevant to the Cospas-Sarsat Programme, so that terms, definitions and abbreviations can be standardized in the three official languages of the Programme (English, French and Russian). Some of these terms are specific to the Cospas-Sarsat Programme, while other general ones are also included to complete the list of terms used in Cospas-Sarsat administrative, operational and technical documents.
- LEOSAR/GEOSAR/MEOSAR Satellites Status
Current Space Segment Status and SAR Payloads for LEOSAR, GEOSAR and MEOSAR satellites.
- GEOSAR Satellite Coverage Map
Map with operational GEOSAR satellite coverage and GEOLUTs. GEOSAR: satellites in Geostationary Earth Orbit for Search and Rescue . With a list of GEOLUTs (LUT: Local User Terminals on earth).
- LEOSAR Satellite Coverage Map
Map with operational LEOSAR satellite coverage and GEOLUTs. LEOSAR: satellites in Low-altitude Earth Orbit for Search and Rescue. With a list of LEOLUT (LUT: Local User Terminals on earth).
- Register Your Beacon
Register Your Beacon and Make the Difference Between Life and Death! By registering your beacon, you allow search-and-rescue authorities in an emergency to retrieve crucial information about you and your emergency contacts (Help and FAQ).

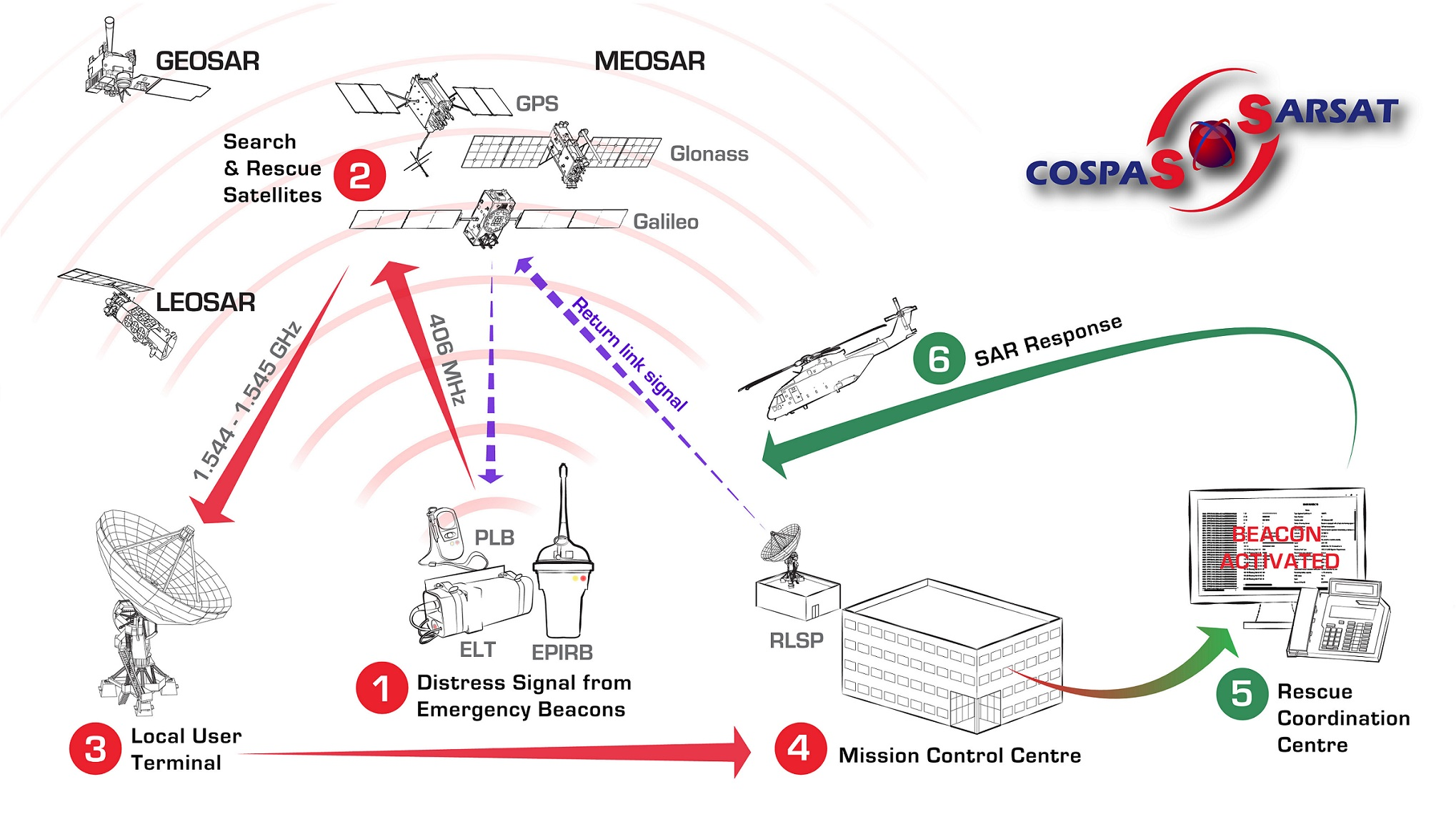
- Conception générale du système Cospas-Sarsat
Le concept de base du système Cospas-Sarsat pour la recherche et le sauvetage : Radiobalises de détresse (406 MHz), LEOSAR, GEOSAR, MEOSAR, Stations terriennes de réception (LUT), Centres de Contrôle de Mission (MCC).
- Introduction au système Cospas-Sarsat
Ce document présente le Système Cospas-Sarsat aux utilisateurs potentiels. Il s’agit d’un système de communication destiné à faciliter les opérations de recherches et de sauvetage (Search and Rescue ou SAR) partout dans le monde, basé sur des alertes émises par des balises et captées au moyen de satellites. Le Système utilise des engins spatiaux et des installations au sol pour détecter et localiser les signaux émis par les balises de détresse équipant des navires et des aéronefs, ou transportées par des particuliers. Les informations d'alerte comprennent la position de la balise et d'autres informations connexes telles que les informations fournies lors de l'enregistrement de celle-ci dans une base de données. Elles sont envoyées par Cospas-Sarsat aux services SAR concernées. La famille des balises de détresse comprend les émetteurs de localisation d'urgence (ELT, destinés à être utilisés en avion), les radiobalises de localisation de sinistre (EPIRB, destinées à être utilisées sur des navires) et les balises de localisation personnelles (PLB, utilisées dans plusieurs environnements par des particuliers).
- Transition vers le système MEOSAR
Le Programme international Cospas-Sarsat a initié le développement d’un système de satellites orbitant autour de la Terre à moyenne altitude pour la recherche et le sauvetage (système MEOSAR), avec des répéteurs SAR (Search and Rescue) placés sur les satellites des systèmes de navigation mondiale européen (Galileo), russe (Glonass) et américain (GPS). Le système MEOSAR sera initialement un complément aux deux systèmes satellites déjà existant LEOSAR (en orbite basse) et GEOSAR (géostationnaires) et remplacera éventuellement le système LEOSAR.
- Foire aux Questions (FAQ) pour les Balises
Une balise de détresse est un petit émetteur radio qui peut aider les autorités de sauvetage à vous localiser si vous l’activez dans une situation où votre vie est en danger. Lorsqu’une balise de détresse est activée, celle-ci transmet un signal sur 406 MHz qui peut être détecté par satellite. Des satellites traitent, archivent et retransmettent les émissions des balises qui sont ensuite traitées par une station de réception au sol. La position est calculée puis transmise aux autorités de sauvetage. Une balise EPIRB (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon), en français radiobalise de localisation de sinistre (RLS), est à usage maritime. Foire aux Questions (FAQ) sur les balises de détresse, l'enregistrement et le dépannage.
- État des satellites LEOSAR/GEOSAR/MEOSAR
État actuel du segment spatial et des charges utiles SAR pour les satellites de type LEOSAR, GEOSAR et MEOSAR.
- Couverture des satellites GEOSAR
Carte avec les zones de couverture des satellites GEOSAR opérationnelles. GEOSAR: satellites en orbite géostationnaire pour la recherche et le sauvetage. Avec une liste des GEOLUT (LUT: terminaux locaux).
- Couverture des satellites LEOSAR
Carte avec les zones de couverture des satellite LEOSAR opérationnelles. LEOSAR: satellites en orbite terrestre basse pour la recherche et le sauvetage. Avec une liste des LEOLUT (LUT: terminaux locaux).
- Enregistrez votre balise
Enregistrer votre balise et faites la différence entre la vie et la mort. En enregistrant votre balise, vous autorisez, en cas d’urgence, les autorités en charge des recherches et du sauvetage à utiliser les informations cruciales vous concernant vous et vos contacts d’urgence (Aide et FAQ).

- Cospas-Sarsat system overview
East Asia Hydrographic Commission (EAHC)
- South China Sea Electronic Navigational Charts (SCS ENC)
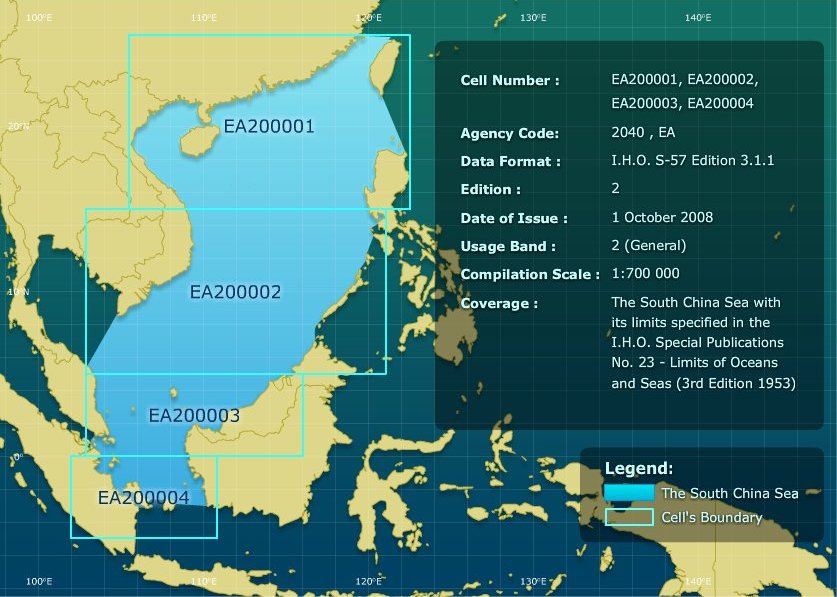
The EAHC produce small scale (1:700.000) official Electronic Navigational Charts (ENC) of the South China Sea to serve the maritime community. Presently, the EAHC has nine Member States (MSs) : China, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. The EAHC decided to provide the SCS ENC to users free of charge. To download the SCS ENC, user has to register with the EAHC.

- South China Sea Electronic Navigational Charts (SCS ENC)
International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA)
- IALA Technical Documents Catalogue
The Technical Documents Catalogue covers the technical guidance and contains an overall view of the IALA standards, recommendations, guidelines, manuals and model courses in force with summary.
- List of Publications
Online publications of the IALA about AtoN, AIS, eNAV, VTS... Categories: Guidelines, Manuals, Model courses, Other Publications, Radio-Navigation Services, Recommendations, Reports and Proceedings.
- NAVGUIDE - Marine Aids to Navigation Manual

This manual is designed to help Marine Aids to Navigation (AtoN) authorities with the harmonization of AtoN services by providing a comprehensive reference guide on all aspects of the service. Additionally, it refers to more detailed guidance from other IALA documents and related international organizations on specific topics. This comprehensive guide offers practical guidance and best practices for the installation, operation, and maintenance of Marine Aids to Navigation and related services. The structure of NAVGUIDE Ed 9.0 conforms to the standards and incorporates the latest advancements in AtoN technology, including enhancements in digital systems and the integration of new devices such as Mobile AtoN and Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS). Moreover, the guide addresses a multitude of updates made by the committee over the past five years, covering aspects such as training components, AtoN services in extreme weather conditions, and an increased focus on sustainability, cybersecurity, and the adoption of autonomous systems within the maritime industry (IALA NAVGUIDE Manual, 2023). - Guía de navegación - Manual de ayudas a la navegación (2014)
La Guía de navegación (Manual AISM) ha sido un documento emblemático y una fuente de información para los miembros y usuarios de la IALA durante muchos años. El objetivo de este manual es apoyar a las autoridades en Ayudas a la Navegación (AtoN) en la unificación de las ayudas a la navegación marítima, proporcionando un primer punto de referencia en todos los aspectos de prestación de estos servicios. La edición 2014 de la Guía realiza una actualización con la información más reciente y los avances en el campo de las Ayudas a la Navegación, su tecnología y aplicación (2014).
- The use of pictograms on aids to navigation (G1122)
A pictogram is a symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. There has been a proliferation in the use of Special Marks in some regions as ‘general purpose’ aids. This guideline provides general information on the design of pictograms on Special Marks and specifies pictograms for the purposes of informing mariners on smaller vessels (IALA guideline G1122).
- The use of AtoN in the design of fairways (G1078)
The purpose of this Guideline is to give guidance for AtoN providers and competent authorities on the: Use of AtoN in the design of fairways, including dredged channels and canals; Review of existing AtoN for fairways including dredged channels and canals. The objective is to define a suitable AtoN mix that enables safe and efficient vessel passage in the most cost effective way for AtoN providers (IALA guidance 1078).
- Daymarks for Aids to Navigation (G1094)
This guideline provides a general informative overview of the main factors that need to be considered when providing and designing a daymark. It points out the aspects of visual perception and how to optimise the identification of a daymark (IALA guideline 1094).
- Les marques de jour comme aide à la navigation (G1094)
Ce guide propose une vue d'ensemble des principaux facteurs qui affectent l'évidence des marques de jour comme aides à la navigation maritime. Il donne aussi quelques éléments pour concevoir de manière optimale une marque de jour sous l'angle de la perception visuelle (Guide AISM 1094, 2012).
- Vessel Traffic Services Manual (VTS Manual)

The purpose of VTS is to contribute to safety of life at sea, safety and efficiency of navigation and the protection of the environment within the VTS area by mitigating the development of unsafe situations. The VTS Manual provides a source of reference on the establishment and provision of VTS for all stakeholders. It also provides a pointer to the suite of IALA Standards related to VTS and the associat-ed Recommendations, Guidelines, Model Courses that any VTS professional may seek. The VTS Manual is intended to complement IALA documentation relating to VTS. It provides a roadmap to assist authorities meet their obligations for the establishment and operation of VTS in a consistent manner (IALA VTS Manual, 2022). - VTS VHF Voice Communication (G1132)
This guideline is intended to engage and support all VTSOs, new and experienced, in promoting best practice in effective VTS radio voice procedures. Furthermore it assists competent authorities, VTS authorities and training organisations when developing standardised operating procedures on communication. It provides guidance that aims to ensure consistency amongst VTSOs when communicating on the VHF (IALA guideline G1132).
- IALA Documentation Relating to VTS
The objective of this reference list is to provide standard documentation for Competent Authorities, VTS Authorities and VTS Training Organisations on IALA documentation (Standards, Recommendations, Guidelines and Model Courses) specifically related to the development, implementation and operation of VTS (IALA reference list).
- IALA Maritime Buoyage System (R1001)
Maritime Buoyage System (MBS) and Other Aids to Navigation (AtoN). Contents: Historical background - General Principles of the System - Rules - Map showing Regions A & B (IALA recommendation R1001).
- Sistema de balizamiento marítimo IALA (Puertos del Estado)

Sistema de balizamiento marítimo y otras ayudas a la navegación, adoptado para las Costas Españolas. Índice: Antecedentes históricos, Principios generales del sistema, Reglas, Mapa de las regiones A y B (AISM-Puertos del Estado, 2010). - An Overview of AIS (G1082)
AIS (Automatic Identification Systems) was developed to provide automatic reporting between ships and to shore, which contributes to the safety of navigation and facilitates traffic management by exchanging information such as identity, position, time, course and speed, autonomously and continuously. This guideline provides an introduction to AIS at an overview level for shore authorities and references relevant documentation where further information can be found (IALA guideline 1082).
- Guidelines about AIS
These documents provide detailed, in depth information about AIS, indicating options, best practices and suggestions for implementation. Guidelines: An Overview of AIS, Application of AIS AtoN on Buoy, Implementation of Application-Specific Messages...
- Recommendations about AIS
These documents represent the highest level of IALA documentation (they would relate to a ‘standard’ in an intergovernmental organisation). Recommendations: AIS Service - main document, Basic AIS Services, AIS References & Glossary of terms and Abbreviations, Use of the AIS in Marine Aids to Navigation Service... AIS for harbours and VTS.
- The Provision of Shore Based Automatic Identification System (AIS) - Provides high level indication of the need for AIS Base Stations (IALA recommendation A-123)
- The AIS service - Initial concepts of AIS Base Stations, Repeaters and Limited Base Stations (IALA recommendation A-124)
- AIS References, Glossary of terms and Abbreviations (IALA recommandation A-124 Appendix 0)
- The Use of the AIS in Marine Aids to Navigation Services - Initial information for using AIS as an AtoN (IALA recommendation A-126, draft)
- Provision of Virtual Aids to Navigation (G1081)
A Virtual AtoN does not physically exist but is a digital information object (symbol and text information) promulgated by an authorized service provider that may be presented on navigational systems. This is used to mark an object other than an existing AtoN or a non-object, such as a reference point in the water or on land. The concept of Virtual AtoN has its roots in AIS, but in the future other means of transmission and presentation may evolve. This Guideline will assist shipmasters, pilots, mariners, private AtoN owners and shore-based competent authorities in realizing the benefits, limitations and the inherent risks involved when using Virtual AtoN as a means of verifying their position and determining a safe course to steer or avoiding dangers (IALA guideline G1081, 2021).
- Ayudas virtuales a la navegación (G1081)
Además de la información proporcionada sobre el uso de ayudas virtuales, esta guía pretende orientar sobre sus riesgos y beneficios, los criterios para su aplicación y el proceso de notificación. También trata del proceso de identificación, la visualización, los métodos de provisión y aplicación, las normas y guías aplicables a ellas, su disponibilidad e integridad, y las cuestiones jurídicas que les atañen. El origen del concepto de “ayuda virtual a la navegación” está en los Sistemas de Identificación Automática (AIS). Sin embargo, se prevé que en el futuro se desarrollarán otros medios de transmisión y presentación. Las referencias a los Sistemas de Identificación Automática (AIS) que figuran en este documento no deben interpretarse como la limitación de las ayudas virtuales a la navegación a sólo ese sistema (Guía de la IALA G1081).
- VDES FAQ
Questions and answers about the VDES: What does VDES stand for?, VHF Data Exchange System (VDES), What is VDES?, What is the difference between VDES and AIS?, Why VDES?, What frequencies does VDES use?, What is the roadmap for VDES?, Are there any VDES test beds?, Where can I find more information on VDES?, Who are the users of VDES, How does an IALA member prepare for VDES?, What are the benefits of the satellite component of VDES?.
- VHF Data Exchange System (VDES) Overview (G1117)

The VHF Data Exchange System (VDES) is seen as an effective and efficient use of radio spectrum, building on the capabilities of AIS and addressing the increasing requirements for data through the system. New techniques providing higher data rates than those used for AIS is a core element of VDES. Furthermore, VDES network protocol is optimized for data communication so that each VDES message is transmitted with a high confidence of reception. VDES increases the capability for digital data exchange in a manner similar to AIS, which includes provision of data to vessels in a geographic area (broadcast), to a specific vessel or a group of vessels in a geographic area (addressed) or to a fleet of vessels (addressed). This Guideline provides an introduction to the VHF Data Exchange System (VDES) at an overview level. It does not include technical details. This document is intended to assist in the understanding, development and promotion of VDES (IALA guideline G1117) - Risk Management Methodology for AtoN (G018)
This Guideline is intended to outline a general description on risk management methodology for marine Aids to Navigation (AtoN) including Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) through the analysis of all the hazards in a waterway so that all transit risks are effectively managed by AtoN authorities (IALA Guideline G1018).
- Providing AtoN Services in Polar Regions (G1108)
In view of the recent opening of shipping routes and the increase in number of voyages in Polar Regions, it is clear there is a need to provide guidance on the special challenges of providing AtoN services in Polar Regions. This Guideline addresses these specific challenges and it is assumed that all other aspects of AtoN provision are dealt with in existing IALA documentation (IALA guideline 1108).
- IALA World Wide Radio Navigation Plan
This IALA World Wide Radio Navigation Plan aims to build on individual National and Regional plans and identify the Radio Navigation components which will be key to the successful implementation of e-Navigation. One of the cornerstones of e-Navigation is the universal availability of robust position-fixing, navigation and timing services. This document focuses solely on the need to provide robust electronic position, navigation and timing (PNT) information, primarily via radio navigation systems. It presents the IALA position on current, developing and future PNT systems within the maritime environment (2012).
- IALA Maritime Radio Communications Plan (MRCP)

This Maritime Radio Communications Plan (MRCP) has been developed by IALA to assist in the selection of radio communication systems required to support e-Navigation and GMDSS. The current status of radio communication in the maritime mobile bands is discussed and forms the basis of projections for future developments needed to support e-navigation, GMDSS and the development of Maritime Autonomous Systems (Surface). The core objective of the Maritime Radio Communications Plan (MRCP) is to state the IALA vision for the efficient use of Radio Spectrum in the Maritime Mobile Service. Edition 3 of the MRCP reflects the outcomes of developments in maritime radio communication spectrum. This document focuses on the need for an agreed infrastructure of communications between ships and ashore. It presents IALA’s view on current, developing and future Radio Communication Systems for the maritime sector. - World DGNSS Stations List
Table of DGNSS Stations (Differential Global Navigation Satellite System). IALA radiobeacon DGNSS is a means of providing differential GNSS (DGPS at present) corrections and integrity information to maritime users. Also 2015 version.
- Systems and Services for High Accuracy Positioning and Ranging
The purpose of this document is to provide an overview about systems and services enabling high‐accuracy positioning or ranging in specific areas such as waterways, traffic separation schemes, traffic zones with limited manoeuvring space, ports and harbours, and congested waters with increased risks of collisions or groundings. In this Guideline the term “high‐accuracy positioning and ranging” refers to accuracies at sub‐metre level (IALA guideline G1127).
- GNSS Vulnerability and Mitigation Measures
This document considers all types of GNSS vulnerability within the maritime field, and the mitigation measures that may be used to overcome them. The effect on marine navigation of interruptions to GNSS will be significant. Where natural events, such as space weather, affect GNSS signal reception, it is likely that the effects will be observed over large areas and during any phase of navigation. Man-made interference is most likely to arise within coastal waters, since the sources of man-made interference are likely to be land-based and will be restricted to line-of-sight. However, the possibility of deliberate shipborne or airborne jamming cannot be ruled out (IALA recommendation R129).
- The Technical Approach to Establishing a Maritime eLoran Service
Service providers are opting to provide eLoran services as part of a robust PNT solution, as eLoran is dissimilar and complementary to GNSS services. The aim of this Guideline is to enable service providers to deliver, monitor and assess the performance of eLoran services in a common manner (IALA guideline G1125, 2017).
- Port Traffic Signals (R0111)
Principles of the system of port traffic signals. It is intended that the rules for Port Traffic Signals shall be followed to control traffic movements in ports and port approaches (IALA recommendation R0111/E111).
- International Dictionary of Marine Aids to Navigation - IALA Dictionary
The International Dictionary of Marine Aids to Navigation (AtoN), also known as "the IALA Dictionary", provides a listing of words and phrases used to explain and describe planning, operations, management, equipment, systems and scientific terms relevant to AtoN. This is an HTML, wiki-based dictionary.

- IALA Technical Documents Catalogue
Organisation Hydrographique Internationale (OHI)
- Catalogue des publications en ligne
Catalogue des publications en ligne : Publications bathymétriques, Publications sur le renforcement des capacités, Publications mixtes, Normes et Spécifications, Autres Publications, Publications périodiques, Projets de publications.
- Symboles, abréviations et termes utilisés sur les cartes marines (INT 1)
On trouve dans ce document (ouvrage 1D du SHOM) l’ensemble des symboles, abréviations et termes utilisés sur les cartes marines aux normes internationales. Cette ouvrage s’applique aux cartes marines imprimées. Les symboles et abréviations affichés sur les écrans de navigation utilisant des cartes marines électroniques peuvent parfois différer de ceux décrits dans cet ouvrage.
- Normes en vigueur de l'OHI pour les ECDIS et ENC
Normes de l'OHI les plus récentes s'appliquant aux ECDIS - Normes de l'OHI les plus récentes s'appliquant aux producteurs d'ENC (Services hydrographiques). Titres : Dispositif de l'OHI pour la protection des données - Guide pour la production, la mise à jour et la diffusion des ENC.
- Règlement pour les cartes internationales (INT) et spécifications pour les cartes marines, de l'OHI (S-4)
La carte internationale a été conçue pour faciliter la production d'un portefeuille minimal de cartes marines adaptées aux besoins de la navigation internationale (navires au long cours). Ces cartes de conception internationale permettront aussi aux états membres de l'OHI qui produisent ou désirent produire des cartes couvrant des zones extérieures à leurs eaux nationales, de reproduire en fac-similé, avec uniquement de légères modifications, les cartes modernes choisies conformément à un accord bilatéral entre les états membres.
- Manuel conjoint OMI/OHI/OMM sur les renseignements de sécurité maritime (S-53)

Les renseignements sur la sécurité maritime sont d'une importance primordiale pour tous les navires. Il est donc essentiel d'appliquer des normes communes à la collecte, à la mise en forme et à la diffusion de ces renseignements. Ce n'est qu'à cette condition que les gens de mer pourront être certains de recevoir les renseignements dont ils ont besoin, sous une forme qu'ils comprendront et ce, dans les plus brefs délais. Le présent manuel constitue un guide pratique pour toute personne concernée par la rédaction des avertissements de navigation ou par la diffusion de prévisions et d'avertissements météorologiques dans le cadre du système mondial de détresse et de sécurité en mer (SMDSM). - Limites des océans et des mers, 1953 (S-23)
Dans cette troisième édition de 1953 les limites proposées sont décrites au cours du texte et représentées sur trois feuilles. Ces limites ont été établies uniquement pour les besoins des Services hydrographiques nationaux et n’ont aucune signification politique.
- Carte mondiale (feuille 1) - Méditerranée (feuille 2) - Indonésie (feuille 3)
- Documents de l'OMI relatifs à la navigation électronique
L'e-navigation est définie comme la collecte, l'intégration, l'échange, la présentation et l'analyse harmonisés des renseignements maritimes à bord et à terre par des moyens électroniques afin d'améliorer la navigation d'un poste d'amarrage à l'autre et les services connexes pour la sûreté et la sécurité en mer et la protection du milieu marin. Elle vise à répondre aux besoins actuels et futurs des utilisateurs par l'harmonisation des systèmes de navigation maritime et des services de soutien à terre.
- Dictionnaire hydrographique international (S-32)
Le Dictionnaire hydrographique international (S-32) est un dictionnaire multilingue qui est la référence faisant autorité pour les termes et définitions liés à l'hydrographie utilisés dans les normes, spécifications et autres publications informatives de l'OHI. Cette base de données de dictionnaire en ligne comprend des termes et définitions harmonisés pour les langues suivantes : anglais, français, espagnol, chinois et indonésien. Le dictionnaire est géré par le Groupe de travail sur le dictionnaire hydrographique (HDWG), qui est un organe subsidiaire du Comité des services et des normes hydrographiques (HSSC) de l'OHI.
- Annuaire de l'OHI (P-5)
Liste des états membres de l'OHI et des états non membres.
- États membres de l'OHI
Carte des états-membres de l'OHI.
-->
- Catalogues de cartes en ligne des Etats membres de l'OHI
Les tables suivantes fournissent des liens avec les catalogues de cartes en ligne des États membres de l'OHI. Pays: Allemagne, Argentine, Australie, Belgique, Brésil, Canada, Chili, Colombie, Danemark, Équateur, Estonie, France, Géorgie, Grèce, Hong Kong Chine, Islande, Inde, Indonésie, Italie, Japon, Afrique du Sud, Corée (Rép. De), Lettonie, Malaisie, Mexique, Maroc, Pays-Bas, Norvège, Nouvelle-Zélande, Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinée, Pérou, Pologne, Portugal, Singapour, Espagne, Suède, Ukraine, Royaume-Uni, États-Unis.
- Carte générale bathymétrique des océans (GEBCO)
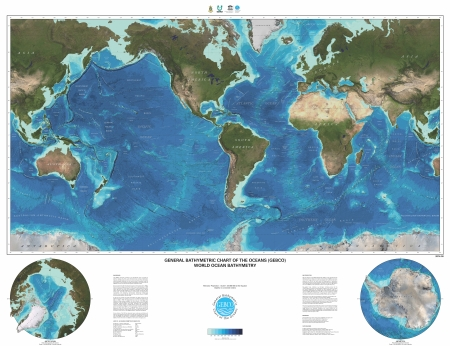
La carte GEBCO mondiale donne la bathymétrie des fonds marins sous la forme d'un carte de 1,3m par 1,0m avec des teintes hypsométriques. La carte est en projection de Mercator à l'échelle de 1:35,000,000 à l'équateur (Carte scannée téléchargable, format PDF et GeoTIFF). Il existe aussi des cartes bathymétriques en PDF pour l'océan Artique (IBCAO) et pour l'océan Austral (IBCSO).
- Catalogue des publications en ligne
International Hydrographic Organization (IHO)
- Catalog of online publications
Catalog of online publications: Bathymetric Publications, Capacity Building Publications, Miscellaneous Publications, Periodical, Standards and Specifications, Other Publications and Draft Publications
- Facts about Electronic Charts and Carriage Requirements (S-66)
Feedback from those involved in the use of charts and electronic charting systems indicates a requirement to provide guidance on the regulations and the status of equipment that is available in the market today. This document has been produced to help clarify some of the uncertainties.
- Mariners’ Guide to Accuracy of Depth Information in Electronic Navigational Charts (S-67)
IHO publication S-67 “Mariners Guide to Accuracy of Depth Information in ENC” is a guide to navigators, and navigator training organizations, on the degree of confidence they should have in the adequacy and accuracy of charted depths and their positions in an Electronic Navigational Chart. The intended readers for this document are navigators on coastal or international voyages; and organizations training navigators for these voyages (More information).
- Information on ENC Generalization, Over-Scaling and Safety Checking Functions in ECDIS
To help mariners better assess the information presented on on-board navigation systems and understand what this can represent at sea, the IHO has released a new paper on Electronic Navigational Chart (ENC) Generalization, Over-Scaling and Safety Checking Functions in Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS). For centuries, marine cartographers have been using generalization techniques to transform our view of the world from a true three-dimensional reality to a scaled, two-dimensional abstract view. This new publication is designed to help users gain a better understanding of classification, simplification, exaggeration, symbolization and scale in charts, and how they should use this information while navigating. Created by the IHO ENC working Group (ENCWG), the paper was drafted following comments from mariners, and is designed to improve users’ ECDIS familiarisation.
- Current IHO ECDIS and ENC Standards
Latest IHO Standards that apply to ECDIS Equipment - Latest IHO Standards that apply to ENC Producers (Hydrographic Offices). Titles: Chart Content and Display Aspects of ECDIS - Presentation Library for ECDIS - Data Protection scheme...
- Specifications for Chart Content and Display Aspects of ECDIS (S-52)
The IHO has produced Specifications for the Chart Content and Display Aspects of ECDIS, publication S-52, in order to ensure that hydrographic data supplied by its Member States' HO is used in a manner that will enhance the safety and efficiency of navigation by satisfying the requirements set out in the IMO Performance Standards for ECDIS. The publicatio, describes the requirements and methods in relatively general terms.
- Description of symbols for use on ECDIS (S-52, Annex A)
The ECDIS Presentation Library as a separate document, gives full details of colours, symbols, symbolization instructions, etc. together with guidance on how an ENC should be displayed.
- IHO Transfer Standard for Digital Hydrographic Data - ENC (S-57)
The publication "S-57-IHO" Transfer Standard for Digital Hydrographic Dataâ describes the standard to be used for the exchange of digital hydrographic data between national hydrographic offices and for its distribution to manufacturers, mariners and other data users. For example, this standard is intended to be used for the supply of data for ECDIS. This transfer and distribution has to take place in such a way that none of the meaning of the data is lost. For S-57 see also:
- Information about ENCs and the associated standards (IHO)
- S-57 ENC Object Catalogue (Teledyne CARIS)
- S-57 ENC Object and Attribute Catalogue (HydroService AS/Jeppesen)
- Product Specification for Raster Navigational Charts - RNC (S-61)
The elements of this product specification define the minimum requirements a Raster Navigational Chart (RNC) must have to satisfy the draft performance standard for a Raster Chart Display System (RCDS). This product specification does not define underlying raster data structures of a raster navigational chart. The national hydrographic office producing the raster navigational chart should select that data structure.
- IHO Test Data Sets for ECDIS
The IHO Publication S-64 comprises an Instruction Manual and numerous ENC Test Data Sets. The S-64 data sets contain both encrypted and unencrypted ENC cells and Raster Navigational Chart (RNC) data. The IHO Test Data Sets (TDS) for Electronic Chart and Display Information System (ECDIS) have been produced to fulfil the requirement for a data set necessary to accomplish all ECDIS testing requirements as outlined in the IEC 61174 standard.
- Regulations for International (INT) Charts and Chart Specifications of the IHO (S-4)
The aim of the international chart concept is to facilitate the provision of minimum sets of charts suitable for the navigational requirements of international (foreign-going) shipping. Such internationally-conceived charts will also enable those IHO Member States who provide, or wish to provide, charts outside their own national waters, to print by facsimile reproduction with only superficial modifications, selected modern charts under the terms of a bilateral arrangement between the Member State.
- Joint IMO/IHO/WMO Manual on Maritime Safety Information (S-53)
Maritime safety information is of vital concern to all ships. It is therefore essential that common standards are applied to the collection, editing and dissemination of this information. Only by doing so will the mariner be assured of receiving the information he needs, in a form which he understands, at the earliest possible time. This manual provides a practical guide for anyone who is concerned with drafting navigational warnings or with the issuance of meteorological forecasts and warnings under the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS). Also JCOMM upload.
- IHO Universal Hydrographic Data Mode (S-100)
S-100 provides a contemporary hydrographic geospatial data standard that can support a wide variety of hydrographic-related digital data sources, and is fully aligned with mainstream international geospatial standards, in particular the ISO 19100 series of geographic standards, thereby enabling the easier integration of hydrographic data and applications into geospatial solutions.
- ENC Product Specification (S-101)
- IMO E-Navigation Documents
E-navigation is defined as “the harmonized collection, integration, exchange, presentation and analysis of marine information on board and ashore by electronic means to enhance berth to berth navigation and related services for safety and security at sea and protection of the marine environment.”
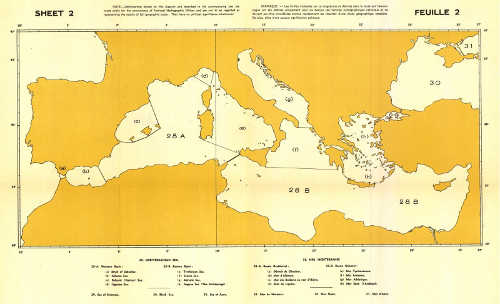
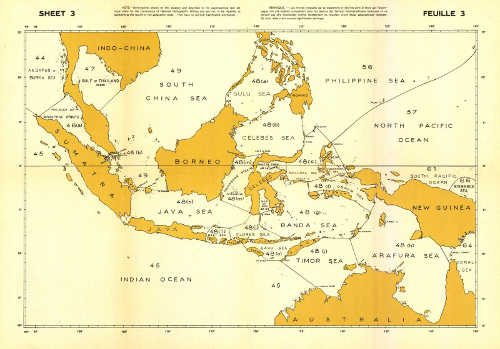
- Limits of Oceans and Seas, 1953 (S-23)
In this 3rd edtion of 1953 the limits proposed are described in the text and shown in the three accompanying sheets. These limits have been drawn up solely for the convenience of National Hydrographic Office and have no political significance whatsoever.
- World Chart (sheet 1) - Mediterranean (sheet 2) - Indonesia (sheet 3)
- Limits of Oceans and Seas, draft 2002 (S-23)
This draft 4th edition of S-23 was developed from 1998 to 2002, based on the 1986 draft. It was submitted to IHO Member States in August 2002 for approval, but the voting process was interrupted by the IHB directing Committee in September 2002. It is a working document only. The 2002 draft 4th edition of S-23 was organized in ten regional chapters. The limits described in this publication have been drawn up solely for hydrographic purposes. It must not be construed as having any legal or political connotation whatsoever.
- International Hydrographic Dictionary (S-32)
The International Hydrographic Dictionary (S-32) is a multi-language dictionary that is the authoritative reference for hydrographic related terms and definitions used in IHO standards, specifications and other informative publications. This online dictionary database includes harmonised terms and definitions for the following languages; English; French; Spanish; Chinese and Indonesian. The dictionary is maintained by the Hydrographic Dictionary Working Group (HDWG), which is a subsidiary body of the Hydrographic Services and Standards Committee (HSSC) of the IHO.
- IHO Yearbook (P-5)
List of member states of the IHO and of non-member states.
- IHO Member States Online Chart Catalogues
The following table provides links to IHO Member States online Chart Catalogues. Countries: Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Croatia (Republic of), Denmark, Ecuador, Estonia, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong China, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Korea (Rep. of), Latvia, Malaysia, Mexico, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Poland, Portugal, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Ukraine, UK, USA.
- INT Chart & ENC Web Catalogues (S-11 B)
IHO developed a web service in order to efficiently provide the current status of charts that coastal states produce and distribute for users. This service helps not only mariners but chart users to search charts in various ways and to display them on several base maps. In this way, mariners and users will be quickly and easily able to search charts and get relevant information. Catalogues: ENC Coverage Catalogue shows ENC data limits, ports and International (INT) Chart boundaries. IHO Web Catalogue of INT Charts shows existing and planned INTernational charts.
- Backup Paper Charts
At the references the Maritime Safety Agencies of coastal States were requested, in coordination with their Hydrographic Offices, to provide information to the IHO regarding their recommendations for the paper charts to be carried: a. As a backup to a single ECDIS using ENCs; and b. For use when ECDIS is used in the Raster Chart Display Mode (RCDS). The information provided by coastal States is available as pdf files by clicking on the State´s name below. Only States which have provided information are included.
- General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO)
The GEBCO world map shows the bathymetry of the world's ocean floor in the form of a 1.3 m by 1.0 m shaded relief colour map. The map is on a Mercator projection at a scale of 1:35,000,000 at the Equator (Raster map for upload, JPEG file). Further there are Bathymetric PDF charts for the Arctic Ocean (IBCAO) and for the Southern Ocean (IBCSO).

- Catalog of online publications
International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Publications catalogue
Today, IMO has over 200 titles available in English. Many are translated into French, Spanish, Arabic, Chinese and Russian.
- Rescue at Sea: A guide to principles and practice as applied to refugees and migrants
The guide is intended for Masters, ship owners, Government authorities, insurance companies, and other interested parties involved in rescue-at-sea situations. It provides guidance on relevant legal provisions, on practical procedures to ensure the prompt disembarkation of rescued persons, and on measures to meet their specific needs, particularly in the case of refugees and asylum-seekers.
- International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS)
Consolidated edition 2004. The SOLAS Convention in its successive forms is generally regarded as the most important of all international treaties concerning the safety of merchant ships. The main objective of the SOLAS Convention is to specify minimum standards for the construction, equipment and operation of ships, compatible with their safety. Contents: I. General Provisions - II-1. Construction-Structure, subdivision and stability, machinery and electrical installations - II-2. Construction-Fire protection,fire detection and fire extinction - III. Life-saving appliances and arrangements - IV. Radio communications - V. Safety of navigation - VI. Carriage of cargoes - VII. Carriage of dangerous goods - VIII. Nuclear ships - IX. Management for the safe operation of ships - X. Safety measures for high-speed craft - XI-1. Special measures to enhance maritime safety - XI-2. Special measures to enhance maritime security - XII. Additional safety measures for bulk carriers - Appendix Certificates (Also 1974 edition).
- Convention internationale de 1974 pour la sauvegarde de la vie humaine en mer (SOLAS)
SOLAS (pour Safety Of Life At Sea, de son nom complet International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea) est un traité international visant à définir différentes règles relatives à la sécurité, la sûreté et l'exploitation des navires. Traduite en français : Pour la Sauvegarde de la vie humaine en mer. Cette convention s'applique en général aux navires de jauge brute supérieure ou égale à 500 UMS qui effectuent des voyages en eaux internationales. Sommaire : I. Généralités - II-1. Construction - Compartimentage et stabilité, machine et installations électriques - II-2. Protection contre l'incendie, détection et extinction - III. Matériel de sauvetage - IV. Radiocommunications - V. Sécurité de navigation - VI. Transport de marchandises particulières - VII. Transport de marchandises dangereuses - VIII. Navires à propulsion nucléaire - IX. Gestion de la sécurité des opérations du navire - X. Mesures de sécurité pour les navires à grande vitesse - XI-1. Mesures spéciales pour améliorer la sécurité des navires - XI-2. Mesures spéciales pour améliorer la sûreté des navires - XII. Mesures de sécurité additionnelles pour les navires transportant des marchandises en vrac - Annexes.
- International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters (Polar Code)
The Polar Code is intended to cover the full range of shipping-related matters relevant to navigation in waters surrounding the two poles - ship design, construction and equipment; operational and training concerns; search and rescue; and, equally important, the protection of the unique environment and eco-systems of the polar regions (MEPC 68/21/Add.1 Annex 10: Resolution MEPC.264(68), 2015). More information.
- Guidelines for ships operating in polar waters
Ships operating in the Arctic and Antarctic environments are exposed to a number of unique risks. Poor weather conditions and the relative lack of good charts, communication systems and other navigational aids pose challenges for mariners. When ice is present, it can impose additional loads on the hull, propulsion system and appendages. The Guidelines aim to promote the safety of navigation and to prevent pollution from ship operations in polar waters (Resolution A 26/Res.1024, 2010). Also on Artic Portal.
- Guidelines For Ships Operating in Arctic Ice-Covered Waters
Ships operating in the Arctic environment are exposed to a number of unique risks. The Guidelines aim to promote the safety of navigation and to prevent pollution from ship operations in Arctic ice-covered waters. The Guidelines take into account that Arctic conditions may include sea and glacial ice that can represent a serious structural hazard to all ships. The Guidelines address the fact that the Arctic environment imposes additional demands on ship systems, including navigation, communications, life-saving, main and auxiliary machinery, etc. In addition, the Guidelines recognize that safe operation in such conditions requires specific attention to human factors including training and operational procedures (MSC/Circ.1056 MEPC/Circ.399, 2002).
- Recueil international de règles applicables aux navires exploités dans les eaux polaires (Polar code)
Le Recueil sur la navigation polaire vise à couvrir l'intégralité des questions de transport maritime relatives à la navigation dans les eaux qui entourent les deux pôles – cela comprend la conception, la construction et l'équipement des navires; les problématiques opérationnelles et de formation; la recherche et le sauvetage; et, tout aussi importante, la protection de l'environnement et des écosystèmes uniques des régions polaires (MEPC 68/21/Add.1 Annexe 10 : Résolution MEPC.264(68), 2015).
- Directives pour les navires exploités dans les eaux polaires
Les navires exploités dans les environnements arctique et antarctique sont exposés à un certain nombre de risques sans pareils. Les conditions météorologiques et le manque de cartes marines fiables, de systèmes de communication et d'autres aides à la navigation posent des problèmes aux gens de mer. En présence de glace, des charges supplémentaires peuvent être imposées à la coque, au système de propulsion et aux appendices du navire. Les présentes Directives visent à promouvoir la sécurité de la navigation et à prévenir la pollution par les navires exploités dans les eaux polaires (Résolution A.1024(26), 2010).
- Guide For Cold Water Survival
This guidance is intended primarily for seafarers. It provides information which will help you if you are unlucky enough to fall into cold water, or have to enter it in an emergency, or have to use survival craft in cold conditions. It also provides information which will help seafarers, trained as first-aid providers, to treat those rescued from cold conditions (Circular MSC.1/Circ.1185/Rev.1).
- Leitfaden für das Überleben in kaltem Wasser
Dieser Leitfaden ist hauptsächlich für Seeleute vorgesehen. Er stellt Informationen zur Verfügung, die demjenigen helfen, der unglücklicherweise ins kalte Wasser fällt, in einem Notfall sich in das Wasser begeben muss oder ein Überlebendfahrzeug bei kalten Bedingungen benutzen muss. Er stellt auch Informationen zur Verfügung, die den als Helfer für Erste Hilfe ausgebildeten Seeleuten helfen, diejenigen zu behandeln, die aus kalten Umgebungsbedingungen gerettet wurden (Rundschreiben MSC.1/Circ.1185/Rev.1).
- IMO documents about Communications Systems
IMO resolutions and IMO circulars about communications systems.
- IMO Documents about Communications Procedures
IMO resolutions and IMO circulars about communications procedures.
- GMDSS Master Plan
Master plan of shore-based facilities for the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS). Content: List of DSC coast stations - List of INMARSAT land earth stations - NAVTEX service - The international SAFETYNET service - HF NBDP MSI broadcast service (Circular GMDSS.1/Circ.22, 2018).
- International SafetyNET Manual

Edition 2018. SafetyNET is an international automatic direct-printing satellite-based service for the promulgation of Maritime Safety Information (MSI), navigational and meteorological warnings, meteorological forecasts, Search and Rescue (SAR) information and other urgent safety-related messages to ships. This Manual describes the structure and operation of the International SafetyNET Service. It is intended primarily for national Administrations and registered information providers, but may also be useful to the mariner who requires more operational information than is found in manufacturers' equipment manuals (IMO, MSC.1/Circ.1364/Rev.1, 2016). Also on USCG page the 2012 edition. - International SafetyNET Services
Edition 2019. This Manual describes the structure and operation of the International SafetyNET [and SafetyNET II] Service[s]. As result of changes to the Inmarsat satellite network and services, the fifth revision of the International SafetyNET Manual will be IMO publication MSC.1/Circ.1364/Rev.2.
- Manuel SafetyNET international
Édition 2011. Le service SafetyNET est un service automatique d'impression directe qui consiste à diffuser dans le monde entier, par satellite, des avertissements de navigation, des avis et des prévisions météorologiques, des renseignements utiles pour la recherche et le sauvetage (SAR) et d'autres messages urgents concernant la sécurité (renseignements sur la sécurité maritime - RSM) à l'intention des navires. Le présent Manuel décrit la structure et le fonctionnement du service SafetyNET international. Il s'adresse essentiellement aux Administrations nationales et aux pourvoyeurs de renseignements inscrits, mais il peut également servir aux navigateurs désireux de complèter les renseignements fournis par les constructeurs de matériel dans leur manuel d'exploitation.
- Manual Revisado del Servicio Internacional SafetyNET
SafetyNET es un servicio internacional automático por satélite de impresión directa, destinado a difundir entre los buques radioavisos náuticos y meteorológicos, pronósticos meteorológicos, información sobre búsqueda y salvamento (SAR) y otros mensajes urgentes relacionados con la seguridad (la información sobre seguridad marítima - ISM). En el presente Manual se describe la estructura y el funcionamiento del servicio internacional SafetyNET. Está destinado principalmente a las Administraciones nacionales y los proveedores de información registrados, si bien también puede ser útil para los navegantes que necesiten ampliar la información operacional proporcionada en los manuales de equipo de los fabricantes.
- Revised IMO NAVTEX Manual

NAVTEX is an international automated direct-printing service for promulgation of navigational and meteorological warnings, meteorological forecasts and other urgent information to ships. It was developed to provide a low-cost, simple and automated means of receiving maritime safety information on board ships at sea in coastal waters. This Manual describes the structure and operation of the NAVTEX Service. It is intended primarily for use by Maritime Administrations and others concerned with the preparation and broadcasting of maritime safety information. It will also be of interest to seafarers, shipowners and others who need to receive such information in order to safely go about their business at sea (IMO, MSC.1/Circ.1403/Rev.1, 2016). - Überarbeitete Fassung des NAVTEX Handbuche
NAVTEX ist ein internationaler automatisierter Sofortdruckdienst zur Veröffentlichung von Navigations- und meteorologischen Warnungen, meteorologischen Vorhersagen und anderen dringenden Informationen an Schiffe. Dieses Handbuch beschreibt den Aufbau und die Ausführung des NAVTEX Dienstes. Es ist hauptsächlich für Schifffahrtsverwaltungen und andere Betroffene im Bereich der Erstellung und Aussendung von Maritimen Sicherheitsinformationen vorgesehen. Außerdem wird es für Seeleute, Reeder und andere, die solche Informationen benötigen, um sicher ihrer Arbeit auf See nachgehen zu können, von Belang sein (BSH).
- Manuel NAVTEX révisé
NAVTEX est un service automatique d'impression directe destiné à être utilisé dans le monde entier pour l'émission d'avertissements de navigation, d'avertissements météorologiques, de prévisions météorologiques et d'autres renseignements urgents à l'intention des navires. Le présent Manuel décrit la structure et le fonctionnement du service NAVTEX. Il a été établi essentiellement à l'intention des Administrations maritimes et autres parties s'occupant de la mise au point et de la diffusion de renseignements sur la sécurité maritime. Il s'adresse également aux gens de mer, aux propriétaires de navires et aux autres parties qui ont besoin de ces renseignements pour se livrer à leurs activités en mer en toute sécurité.
- Manual NAVTEX de la OMI
NAVTEX es un servicio internacional automatizado de impresión directa para la difusión de radioavisos náuticos y meteorológicos, pronósticos meteorológicos y otros mensajes de información urgente dirigida a los buques. En el presente Manual se describe la estructura y el funcionamiento del Servicio NAVTEX. Está destinado principalmente a las Administraciones marítimas y otras partes que participan en la preparación y transmisión de información sobre seguridad marítima. También es de interés para la gente de mar, los propietarios de buques y otras personas que necesitan recibir esta información para llevar a cabo sin riesgos sus actividades en el mar.
- Revised Joint IMO/IHO/WMO Manual on Maritime Safety Information (MSC.1/Circ.1310/Rev.1 - 2014)
This manual provides a practical guide for anyone who is concerned with drafting navigational warnings or with the issuance of meteorological forecasts and warnings under the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS). Also 2009 edition on JCOMM upload.
- Manuel Conjoint OMI/OHI/OMM Révisé sur les Renseignements de Sécurité Maritime (F-MSC Circ1310)
Le présent manuel constitue un guide pratique pour toute personne concernée par la rédaction des avertissements de navigation ou par la diffusion de prévisions et d'avertissements météorologiques dans le cadre du système mondial de détresse et de sécurité en mer (SMDSM).
- Manual Conjunto OMI/OHI/OMM Relativo a la Información Sobre Seguridad Marítima (ISM) Revisado (S-MSC Circ1310)
El presente Manual es una guía práctica para todas las personas interesadas en elaborar radioavisos náuticos o en transmitir pronósticos y avisos meteorológicos en el marco del sistema mundial de socorro y seguridad marítima (SMSSM).
- IAMSAR - International Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue Manual, Volume III - Mobile Facilities
IAMSAR volume III: Mobile Facilities. The three-volume IAMSAR Manual provides guidelines for a common aviation and maritime approach to organizing and providing search and rescue (SAR) services. Volume III, Mobile Facilities, is intended to be carried aboard rescue units, aircraft and vessels to help with performance of a search, rescue or on-scene co-ordinator function, and with aspects of SAR that pertain to their own emergencies (Edition 2006). Also view online documents.
- IAMSAR - Manual internacional de los servicios aeronáuticos y marítimos de búsqueda y salvamento, Volumen III - Medios móviles
IAMSAR Volumen III: Medios móviles. Los tres volúmenes del manuel IAMSAR proporcionan orientación sobre un enfoque aeronáutico y marı́timo común para organizar y prestar servicios SAR. La finalidad del volumen III, titulado "Medios móviles" es ayudar a los buques y a las aeronaves en la realización de las operaciones de búsqueda y salvamento o la función de coordinador en el lugar del siniestro, así como en los aspectos de la búsqueda y salvamento (SAR) correspondientes a sus propias situaciones de emergencia. Está previsto que este volumen se lleve a bordo de las unidades, aeronaves y buques de salvamento (2016).
- IMO documents of relevance to SAR (search and rescue)
This page provides maritime or joint rescue coordination centres (MRCC or JRCC), solely for their operational purposes, with a minimum list of documents which are essential for such centres to have in their possession or to have rapid and reliable access to a digital version. The list only covers search and rescue and no other tasks which RCCs may require to perform.
- Guide to recovery techniques
Your part in recovery at sea. As a seafarer, you may have to recover people in distress at sea. This might be someone overboard from your own ship or your ship might be responding to someone else's emergency. You may have little warning, and lives may be in your hands. In many areas of the world, especially when out of range of shore-based search and rescue (SAR) facilities, your ship may be the first, or the only, rescue unit to arrive in time. This guide focuses on recovery and the work you may have to do to achieve it. It is intended to be used as a reference document. You should read it now and you should refer to it again while proceeding to the scene of the emergency, as part of your preparation for the recovery operation. It suggests practical recovery techniques which have been used successfully to recover people in distress at sea (IMO, MSC.1/Circ.1182/Rev.1, 2014).
- Guías sobre técnicas de rescate
Su papel en el rescate el el mar. Como navegante, es posible que usted tenga que rescatar a personas en peligro en el mar. Puede tratarse de alguien que haya caído por la borda de su propio buque o puede que su buque haya acudido al lugar en el que se ha producido un suceso. Es posible que le avisen con poco tiempo y que haya vidas que dependan de usted. En muchas zonas del mundo, particularmente en zonas que están fuera del alcance de los medios de búsqueda y salvamento (SAR) en tierra, puede que su buque sea la primera unidad de salvamento, o incluso la única, que llegue a tiempo. El proceso de rescate es a menudo difícil. La guía se centra en el rescate y en lo que usted puede tener que hacer para lograrlo. Está destinada a ser utilizada como documento de referencia. Debe usted leer la ahora y remitirse a ella mientras se dirija al lugar del suceso a fin de prepararse para las operaciones de rescate. En ella se sugieren técnicas de rescate prácticas que han sido utilizadas con éxito para rescatar a personas en peligro en el mar (OMI, MSC.1/Circ.1182/Rev.1, 2014).
- Basic safety guidance for yacht races or oceanic voyages by non-regulated craft (IMO, MSC.1/Circ.1413, 2012)
- Medical assistance at sea (IMO, A 23/Res.950, 2004)
- Proper use of VHF channels at sea (IMO, A23/Res.A.954, 2004)
- Guidance on distress alerts (COMSAR.1/Circ.45, 2009)
- ...
- Guide to recovery techniques
- IMO Standard Marine Communication Phrases (SMCP)

Edition: 2001 (A 22/Res.918). As navigational and safety communications from ship to shore and vice versa, ship to ship, and on board ships must be precise, simple and unambiguous, so as to avoid confusion and error,there is a need to standardize the language used. These SMCP have been compiled: - to assist in the greater safety of navigation and of the conduct of ship - to standardize the language used in communication for navigation at sea, in port-approaches, inwaterways, harbours and on board vessels and - to assist maritime training institutions in meeting the objectives mentioned above (Also PDF document from 2000). - IMO τυποποιημένες ναυτικές φράσεις επικοινωνίας - SMCP
Η μετάφραση του παρόντος εγχειριδίου έγινε από την αγγλική γλώσσα, με βάση την τελευταία έκδοση του βιβλίου με τίτλο “IMO Standard Marine Communication Phrases” (SMCP, 2002) και βασικός στόχος του είναι να χρησιμοποιηθεί στη διδασκαλία της Αγγλικής γλώσσας. Παράλληλα φιλοδοξεί να αποτελέσει πολύτιμο σύμβουλο για όλους τους αξιωματικούς των πλοίων σε θέματα ναυτικών επικοινωνιώv (Eugenides Foundation).
- Code international pour la sûreté des navires et des installations portuaires (code ISPS)
Entré en vigueur le 1er juillet 2004, en vertu du chapitre XI-2 de la Convention SOLAS, le Code international pour la sûreté des navires et des installations portuaires (ISPS) a depuis constitué la base d'un régime de sûreté complet et obligatoire pour le secteur des transports maritimes internationaux. Le Code se compose de deux sections, une Partie A et une Partie B. D'un côté, la Partie A, à caractère obligatoire, présente des prescriptions détaillées relatives à la sûreté maritime et à la sûreté portuaire auxquelles les Gouvernements, les autorités portuaires et les compagnies maritimes contractants à la Convention SOLAS doivent impérativement adhérer afin d'être en conformité avec le Code. De l'autre, la Partie B du Code fournit un ensemble de recommandations sur les dispositions à prendre pour satisfaire aux prescriptions et obligations définies dans la Partie A (2003).
- Guidance documents relevant to maritime security
Here is a list of guidance documents adopted by IMO which are relevant to maritime security.
- Guidelines on Maritime Cyber Risk Management
These Guidelines provide high-level recommendations for maritime cyber risk management. For the purpose of these Guidelines, maritime cyber risk refers to a measure of the extent to which a technology asset is threatened by a potential circumstance or event, which may result in shipping-related operational, safety or security failures as a consequence of information or systems being corrupted, lost or compromised. Supersedes MSC 1/Circ. 1526, 2016 (MSC-FAL.1/Circ.3. 2017). More information about: Maritime Cyber Risk.
- Guidelines on Maritime Cyber Risk Management
- Guidance documents relevant to piracy
Here is a list of guidance documents adopted by IMO which are relevant to piracy. More information about: Piracy and armed robbery against ships.
- Guidance to shipowners and ship operators, shipmasters and crews on preventing and suppressing acts of piracy and armed robbery against ships
This circular aims at bringing to the attention of shipowners, companies, ship operators masters and crews the precautions to be taken to reduce the risks of piracy on the high seas and armed robbery against ships at anchor, off ports or when underway through a coastal State’s territorial waters. It outlines steps that should be taken to reduce the risk of such attacks, possible responses to them and the vital need to report attacks,both successful and unsuccessful, to the authorities of the relevant coastal State and to the ships’ own maritime Administration. Such reports are to be made as soon as possible, to enable necessary action to be taken (MSC.1/Circ. 1334, 2009). More information about piracy.
- Global Counter Piracy Guidance for Companies, Masters and Seafarers
The purpose of this guidance is to protect seafarers, the ship and cargo and, to facilitate threat and risk assessment and planning for voyages transiting areas where the threat of attack by pirates andarmed robbers exists. This guidance is complementary to other industry regional guidance and that issued by international regional organisations.
- Best Management Practices 4: Gulf of Aden and off the Coast of Somalia (BMP4)
This document is intended to advise Best Management Practices (BMP) to assist companies and ships in avoiding piracy attacks, deterring attacks and delaying successful attacks in the Gulf of Aden (GoA) and off the Coast of Somalia (MSC.1/Circ.1339, 2011). Also: Update for HRA. Superced by BMP5 and MSC.1/Circ.1601.
- Best Management Practices 5: Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea (BMP5)
Best Management Practices (BMP) to deter piracy and enhance maritime security in the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea. The purpose of this publication is to help ships plan their voyage and to detect, avoid, deter, delay and report attacks. Experience has shown application of the recommendations in this publication makes a significant difference to the safety of seafarers. Also update for the limits of the the High Risk Area and a version of BMP5 with one file by section (MSCHOA, 2018).
- Industry Counter Piracy Guidance - Global and Regional
The Maritime Safety Committee had recognized the importance of the Best Management Practices (BMP) and the need to comply with the provisions therein. Also this circulaire contain three BMP: Global Counter Piracy Guidance for Companies, Masters and Seafarers, as set out in annex 1; the revised Best Management Practices (BMP5), as set out in annex 2; and Guidelines for Owners, Operators and Masters for protection against piracy and armed robbery in the Gulf of Guinea region as set out in annex 3 (MSC.1/Circ.1601, 2018).
- Best Management Practices WA: West Africa (BMP WA)
Best Management Practices to Deter Piracy and Enhance Maritime Security off the Coast of West Africa including the Gulf of Guinea. This publication aims to help ships plan their voyage and to detect, avoid, deter, delay and report attacks. Experience has shown application of the recommendations in this publication makes a significant difference to the safety of seafarers (ICS & alt, 2020).
- Regional Guide to Counter Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia
The purpose of this guide is to assist those responsible for the operation of ships trading in Asia including companies, owners, masters, agents and seafarers in avoiding attacks, deterring attacks and delaying attacks, actions when attacked and evidence preservation (ReCAAP, ).
- Guidance on Abduction of Crew in the Sulu-Celebes Seas and Waters off Eastern Sabah
This guidance focuses on the incidents of abduction of crew from ships for ransom in the Sulu-Celebes Seas and waters off Eastern Sabah. It provides the guidance and analysis based on the information collected from past incidents in order to assist the shipping industry and ships to enhance their situation awareness and avoid such incidents. This guidance complements the general guidance contained in the “Regional Guide to Counter Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia” (ReCAAP, 2019).
- Resoluciones Comité MSC de la OMI
El Comité de Seguridad Marítima es el más alto órgano técnico de la Organización. Está integrado por todos los miembros. Entre las funciones del Comité de seguridad marítima se incluye "examinar todas las cuestiones que sean competencia de la organización en relación con ayudas a la navegación, construcción y equipo de buques, dotación desde un punto de vista de seguridad, reglas destinadas a prevenir abordajes, manipulación de cargas peligrosas, procedimientos y prescripciones relativos a la seguridad marítima, información hidrográfica, diarios y registros de navegación, investigación de siniestros marítimos, salvamento de bienes y personas, y toda otra cuestión que afecte directamente a la seguridad marítima" (DIRECTEMAR).
- Resoluciones Comité MEPC de la OMI
El Comité de protección del medio marino, que se compone de todos los Estados Miembros, está facultado para examinar toda cuestión que sea competencia de la organización en relación con la prevención y contención de la contaminación del mar, ocasionada por los buques. Especialmente se ocupa de la aprobación y enmienda de convenios y otras reglas y medidas para garantizar su observancia (DIRECTEMAR).
- Convenios OMI
Lo invitamos a conocer los principales convenios de la OMI (Organización Marítima Internacional) : Convenio Internacional sobre Búsqueda y Salvamento Marítimo de 1979 (SAR), Convenio Internacional sobre la Seguridad de la Vida Humana en el Mar (SOLAS)...
- Relevant IMO ECDIS-ENC Documents / Documents pertinents de l'OMI sur les ECDIS et ENC
Documents : Guidelines for the Presentation of Navigation-related Symbols, Terms and Abbreviations (SN.1/Circ.243) - ECDIS: Guidance for good practice (MSC.1/Circ.1503) - Directives pour la présentation des symboles, termes et abréviations utilisés pour la navigation (F-SN.1/Circ.243) - ECDIS : Guide de bonnes pratiques (F-MSC.1/Circ.1503)...
- ECDIS – Richtlinien für gute Praxis
Wenngleich überaus hilfreiche IMO-Richtlinien zu ECDIS auf diese stufenweise Art entwickelt wurden, war es erforderlich, dass die Informationen nach Möglichkeit zusammengefasst werden, um ECDIS-relevante Richtlinien in einem einzigen Rundschreiben zu haben, das ohne Wiederholungen oder ständige Bezugnahme leicht auf dem neusten Stand gehalten werden kann. Diese Informationszusammenfassung ermöglicht ein klares und eindeutiges Verständnis hinsichtlich der Pflichtausrüstung und der Verwendung eines ECDIS (IMO-Rundschreiben MSC.1/Circ.1503).
- E-Navigation Documents
E-navigation is defined as “the harmonized collection, integration, exchange, presentation and analysis of marine information on board and ashore by electronic means to enhance berth to berth navigation and related services for safety and security at sea and protection of the marine environment.” Documents: Strategy for the development and implementation of e-navigation (MSC 85/26/Add.1 Annex 20) - E-navigation Strategy Implementation Plan (NCSR 1/28 Annex 7) - Guidelines on Software Quality Assurance and Human Centered Design for e-navigation (MSC.1/Circ.1512)...
- Guidelines on fatigue
The Organization has developed these Guidelines on fatigue to assist all stakeholders in better understanding their roles and responsibilities in mitigating and managing the risk of fatigue. The Guidelines provide information on the causes and consequences of fatigue, and the risks it poses to the safety and health of seafarers, operational safety, security and protection of the marine environment. It has been prepared to assist all stakeholders in contributing to the mitigation and management of fatigue. The Guidelines are composed of modules each devoted to an interested party. The modules are as follows: Fatigue - Fatigue and the company - Fatigue and the seafarer - Fatigue, awareness and training - Fatigue and ship design - Fatigue, the Administration and port State Authorities (MSC.1/Circ.1598, 2019).
- Handbook for management of public health events on board ships (WHO)
Competent authorities at ports are responsible for managing events that pose a risk to public health. These events – which may be caused by biological, chemical or radiological agents – may vary greatly in terms of severity, requiring different degrees of response. This document from the World Health Organization (WHO) aims to provide technical advice to competent authorities at the port level for management of public health events on board ships.
- Manuel de gestion des évènements de santé publique à bord de navires (OMS)
Les autorités portuaires compétentes sont responsables de la gestion des évènements qui présentent un risque pour la santé publique. Ces évènements peuvent être dus à des agents biologiques, chimiques ou radiologiques. Ils peuvent varier considérablement en termes de gravité, nécessitant différents niveaux de réponse. Le présent document de l'Organisation mondiale de la Santé (OMS) vise à fournir des conseils techniques aux autorités portuaires compétentes pour la gestion des évènements de santé publique à bord des navires.
- International Medical Guide for Ships / Guide médical international de bord
This guide shows designated first-aid providers how to diagnose, treat, and prevent the health problems of seafarers on board ship. It contains fully updated recommendations aimed to promote and protect the health of seafarers and is consistent with the latest revisions of both the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines and the International Health Regulations. Including the ship's medicine chest (ILO/IMO/WHO).
- International Medical Guide for Ships (2007) - with a Quantification addendum
- ΔΙΕΘΝΗΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟΣ ΟΔΗΓΟΣ ΓΙΑ ΠΛΟΙΑ (2011)
- Международное руководство по судовой медицине (2014) - Приложение
- Guía médica internacional de a bordo (1989)
- Guide médical international de bord (1989)
- Trial Account
You can set up a trial to access our online subscription for these products: SOLAS, MARPOL and the IMO-Vega Database. The trials will be active for two working days from the date they are requested (Weekend are not included). Each trial can only be accessed once every year.
- IMODOCS: IMO official document repository
IMODOCS is the official document repository of the IMO. IMODOCS provides full text of documents and resolutions issued since the late 1990s by the principal organs and committees of the Organization. Selected content is available to the public. A free registration is required. Sales publications are not included here but IMO circulars are available: Sub-Committee on Radiocommunications, Search and Rescue (COMSAR), Circular relating to Global Maritime Distress and Safety Systems — shorebased facilities (GMDSS Master Plan), Circular relating to Maritime Safety Committee on safety matters (MSC)...
- ECDIS – Guidance for Good Practice - MSC.1/Circ.1503 (2015)
- ECDIS – Guide de bonnes pratiques - MSC.1/Circ.1503 (2015)
- Guide for Cold Water Survival - MSC.1/Circ.1185/Rev.1 (2012)
- Guide sur la survie en eau froide - MSC.1/Circ.1185/Rev.1 (2013)
- Guía para la supervivencia en aguas frías - MSC.1/Circ.1185/Rev.1 (2013)
- ...
- Supplements
Supplements for the pulications of the IMO. Please choose a language option for Supplements (English - French - Spanish - Arabic, Chinese and Russian) and download the relevant supplement (pdf files), print it and insert it into your publication.

- Publications catalogue
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Catalogue of publications
ITU is pleased to present the English edition of its Publications Catalogue in PDF format. This edition is updated weekly to give an overview of all available ITU publications. With publications of the general secretariat, radiocommunication sector (ITU-R), telecommunication standardization sector (ITU-T) and telecommunication development sector (ITU-D). Also Online Catalogue.
- Online catalog of maritime publications
Catalog of maritime publications: Manual for use by the maritime mobile and maritime mobile-satellite services (Maritime manual) - List IV: List of coast stations and special service stations - List V: List of ship stations and maritime mobile service identity assignments. Also available on MyITU.
- Radio regulations 2020
The ITU Radio Regulations facilitate equitable access to and rational use of the natural resources of the radio-frequency spectrum and geostationary satellite orbits. They also ensure the availability of the frequencies provided for distress and safety purposes and assist in the prevention and resolution of cases of harmful interference between the radio services of different administrations. The Radio Regulations, Edition of 2020, contains the complete texts as adopted by the World Radiocommunication Conference (Geneva, 1995) (WRC-95) and subsequently revised and adopted by World Radiocommunication Conferences, including all Appendices, Resolutions, Recommendations and ITU-R Recommendations incorporated by reference. The four volumes of the 2020 Radio Regulations are available in all six of ITU's official languages in zipped WORD and pdf formats. Contents: Vol. 1 - Articles, Vol. 2 - Appendices, Vol. 3 - Resolutions and Recommendations, Vol. 4 - ITU-R Recommendations incorporated by reference. Plus map for Appendix 27 Rev. WRC-19. Also available on MyITU.
- Manual for use by the maritime mobile and maritime mobile-satellite services (Maritime manual)
The maritime manual, edition of 2011. This manual reflects the regulatory provisions and the latest decisions concerning the maritime services by ITU conferences (including relevant decisions pertaining to the introduction of new systems and techniques). The manual is required to be carried by stations on board ships (View online documents).
- Volume 1: Practical information

Volume 1 provides descriptive text of the organisation and operation of the GMDSS and other maritime operational procedures. Contents: 1. Introduction - 2. System overview of the GMDSS - 3. The scope of activities and responsibilities - 4. General rules of the GMDSS - 5. Radio procedures - 6. Operational procedures for distress, urgency and safety communications - 7. The use of frequencies - 8. Radio personnel requirements - 9. Identification of stations - 10. Other administrative and operational procedures - 11. Related publications - Annexes.
Maritime manual, volume 1, edition of 2011 Maritime manual, volume 1, edition of 2011 - Volume 1: Practical information
- Amendments and extracts for List IV: List of coast stations and special service stations
Compilation of amendments and extracts. List IV contains important information for the mariner in relation to radiocommunications, including the GMDSS (Global maritime distress and safety system) and CP (Public correspondence) services. Detailed information is provided in relation to the facilities available at each maritime coast radio station, which may provide watch-keeping using digital selective calling (DSC) techniques and radiotelephony (2017).
- Preface and Reference tables
- Abbreviations used in the List (Table 2)
- Coast stations participating in the NAVTEX services (Table 4)
- Compilation of amendments: Coast and special service stations
- Online search for coast stations and special service stations
- Amendments and extracts for List V: List of ship stations and maritime mobile service identity (MMSI) assignments
Compilation of amendments and extracts. This list shall be provided to all ship stations for which a Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) installation is required by international agreement.
- Preface and reference tables
- Symbols which designate classes of ships and other abbreviations (Table 2)
- Description of fields
- Compilation of amendments: Ship Stations and MMSI Assignments
- Online search for ship stations
- Maritime related recommendations (ITU-R series)
This page contains maritime related recommendations (Recommendations ITU-R M series). The ITU-R recommendations constitute a set of international technical standards developed by the Radiocommunication Sector (formerly CCIR) of the ITU.
- Operational procedures for the use of direct-printing telegraph equipment in the maritime mobile service (M.492)
- Morse telegraphy procedures in the maritime mobile service (M.1170)
- Radiotelephony procedures in the maritime mobile service (M.1171)
- Miscellaneous abbreviations and signals to be used for radiocommunications in the maritime mobile service (M.1172)
- ...
- Maritime related reports (ITU-R M series)
ITU-R M series reports, related to maritime radiocommunications. A report is a technical, operational or procedural statement, prepared by a study group on a given subject related to a current question or the results of studies referred to in § 3.3 of resolution ITU-R 1.
- GLobal Administration Data System (GLAD)
GLAD is an online data retrieval-system and a central repository of ITU-R common information concerning administrations and geographical areas.
- Table of international call sign series
- Table of maritime identification digits (MIDs)
- Table of coast station identification numbers
- Summary of allocations
- ...
- Maritime mobile access and retrieval system (MARS)
MARS is a free of charge, online access and retrieval system that allows users to consult the information currently registered in the ITU’s maritime database system.
- Ship stations
- Coast stations and special service stations
- Accounting authority identification codes (AAICs)
- ...
- Catalogue of publications
Union internationale des télécommunications (UIT)
- Catalogue des publications
L'UIT a le plaisir de présenter son Catalogue des publications, désormais mis à jour chaque semaine. Il est disponible en anglais, au format PDF, et donne un aperçu des publications UIT en vigueur. Avec les publications du secrétariat général, du secteur des radiocommunications (UIT-R), du secteur de la normalisation des télécommunications (UIT-T) et du secteur du développement des télécommunications (UIT-D). Catalogue en anglais avec certains ouvrages disponibles en français.
- Catalogue des publications maritimes
Catalogue des publications maritimes : Manuel à l'usage des services mobile maritime et mobile maritime par satellite (Manuel maritime) - Liste IV : Nomenclature des stations côtières et des stations effectuant des services spéciaux - Liste V : Nomenclature des stations de navire et des identités du Service Mobile Maritime assignées. Également disponible avec une recherche.
- Règlement des radiocommunications 2020

Le Règlement des radiocommunications, édition 2020, est composé de 4 volumes. Il contient le texte complet du Règlement des radiocommunications tel qu'il a été adopté par la conférence mondiale des radiocommunications y compris tous les appendices, résolutions, recommandations et les recommandations UIT-R incorporées par référence. Le Réglement est disponible dans les six langues officielles de l'UIT aux formats WORD et PDF. - Recommandations de l'UIT-R consacrées aux service mobile maritime
Les Recommandations UIT-R (anciennement CCIR) constituent un ensemble de normes techniques internationales développées par le Secteur des Radiocommunications de l'UIT. Page en anglais avec certaines recommandations disponibles en français.
- Procédures d'exploitation des équipements télégraphiques à impression directe dans le service mobile maritime (M.492)
- Procédures radiotélégraphiques Morse dans le service mobile maritime (M.1170)
- Procédures radiotéléphoniques dans le service mobile maritime (M.1171)
- Abréviations et signaux divers à employer dans les radiocommunications du service mobile maritime (M.1172)
- ...
- Rapports de l'UIT-R consacrées aux service mobile maritime
Rapports de la série M de l'UIT-R liées aux communications radiomaritimes. Un rapport est un exposé technique, d'exploitation ou de procédure préparé par une commission d'études sur un sujet donné. Un rapport concerne une question dont l'étude est en cours ou bien les résultats des études, études dont il est question au § 3.3 de la résolution UIT-R 1. Page en anglais avec certaines recommandations disponibles en français.

- Catalogue des publications
NATO Shipping Centre (NSC)
- Naval Cooperation and Guidance for Shipping (NCAGS) Guide
NCAGS guide to owners, operators, masters and officers. ATP-02.1 is a publication which provides information to ship owners, operators, masters and officers regarding the interaction between naval forces and commercial shipping. In particular the publication serves as a handbook for the world-wide application of NCAGS principles and procedures that exist to enhance the safety of shipping in times of tension, crisis and conflict.
- Threat to commercial shipping in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is one of the world’s busiest waterbodies. While the region offers safe transit to commercial traffic and entry to the Middle East and beyond via the Suez Canal, regional instability in areas such as Libya and Syria have the potential to spill over into the maritime domain and continues to pose a possible threat to commercial traffic. This Allied Maritime Command assessment provides an update on the threat posed to commercial shipping while transiting the Mediterranean in international waters. However, the risk to vessels when operating in territorial waters, i.e. close to the coast or within confined areas, is clearly elevated due to the opportunity it provides a would be attacker.
- Electronic interference in Mediterranean
GPS interference and possible jamming with potentially dangerous consequences is reportedly occurring in the Eastern Mediterranean in vicinity of Cyprus and the entrance to the Suez Canal since the beginning of 2018.
- BMP West Africa
Best Management Practices (BMP) to deter piracy and enhance maritime security off the Coast of West Africa including the Gulf of Guinea (2020). The maritime security situation off the West Coast of Africa is complex and dynamic. BMP – West Africa (WA) has been produced to help ships and seafarers avoid becoming the victims of maritime security incidents in these waters. This publication aims to help ships plan their voyage and to detect, avoid, deter, delay and report attacks. Experience has shown that application of the recommendations in this publication makes a significant difference to the safety of seafarers. The BMP contained in this publication mitigate the risk from piracy and armed robbery.
- BMP5 Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea

Best management practices (BMP) to deter piracy and enhance maritime security in the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea (2018). Seafarers have encountered different security threats when operating ships in the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Indian Ocean and the Arabian Sea. The purpose of this publication is to help ships plan their voyage and to detect, avoid, deter, delay and report attacks. Experience has shown application of the recommendations in this publication makes a significant difference to the safety of seafarers. The BMP contained in this publication mitigates the risk from piracy and other maritime security threats. The fundamental requirements of BMP: Understand the threat - Conduct risk assessments -Implement ship protection measures - Report - Cooperate. - Industry Reporting Guidance - Arabian Gulf, Strait of Hormuz, and Gulf of Oman
Reporting Guidance for vessels transiting the Arabian Gulf, Straits of Hormuz and Gulf of Oman. This guidance should be posted on the bridge for ease of access to watch officers and covered in watch hand overs.
- Regional Guide to counter Piracy and armed robbery against ships in Asia
Even though the statistics from the different reporting centres vary, the fact is that The Far East, including Malacca Strait, Indonesia and South China Sea, is the area where most of the reported incidents have taken place in 2015.Incidents reaching from theft and robbery in port to hijacking of vessels.
- Survival at Sea for Mariners, Aviators and Search and Rescue Personnels
This document summarizes the current scientific knowledge of sea survival for mariners, aviators, search and rescue technicians and medical staff. The text discusses key issues such as drowning through cold shock and swimming failure induced by immersion in water particularly below 15 Celsius, survival prediction curves and non-freezing cold injuries. Practical advice is given on the causes and treatment of seasickness (NATO/STO/CSO, RTO-AG-HFM-152).
- Maritime Security Charts
NATO Shipping Centre advises all mariners to use and comply with procedures contained in Maritime Security Charts produced by United Kingdom Hydrographic Office.
- Maritime Security: Documents for download
NCAGS Guide to Owners, Operators, Masters and Officers - Best Management Practices for Protection against Somalia Based Piracy.

- Naval Cooperation and Guidance for Shipping (NCAGS) Guide
World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
- GMGSS / Limits of METAREAS - Marine weather services
In the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) Services METAREAs or NAVAREAs are regions of the oceans for which specified nations have the responsibility for the co-ordination of the provision of meteorological and other marine safety information. Show national marine weather services sea area maps and satellite/Navtex/Facsimile broadcasts: Click on METAREAS then click on the Metarea list with roman numerals. Also legacy site.
- Weather Reporting - Information for Shipping (WMO-No. 9, Volume D)

Radio weather forecasts and warnings: frequencies and schedules. This Publication contains Marine meteorology and other related geophysical information necessary for safe and economic conduct of shipping operations, as well as for fishing and other marine activities, is made available to the user by the various Meteorological Services of maritime countries. Contents: Frequencies and schedules for satellite systems (GMDSS SafetyNET Services) and terrestrial systems (Radio Voice broadcasts - NAVTEX - HF NBDP - Radio-facsimile). Also available: Amendments by countries. - Marine weather information for GMDSS
The worlds' oceans have been divided into 21 areas, called METAREAS, for the provision of marine meteorological information and services to shipping.
- Transmission schedule of weather forecast for Metarea on Inmarsat Safetynet (legacy site)
- Map with Metareas: meteorological warnings and forecast
- List of common abbreviations for weather forecast on NAVTEX
- Manual on Marine Meteorological Services - Global aspects (WMO-No. 558)
Click on the book image on the left. This Manual is designed: (a) To specify obligations of Members in the implementation of Marine Meteorological Services (MMS); (b) To facilitate cooperation in respect of the international coordination of MMS, in particular the delivery of the International Maritime Organization (IMO)/WMO Worldwide Met-Ocean Information and Warning Service (WWMIWS); (c) To facilitate cooperation between the World Weather Watch (WWW) and MMS; (d) To ensure adequate uniformity and standardization in the practices and procedures followed to achieve (a), (b) and (c) above. Also available on JCOMM.
- Manuel de l’assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes - Aspects mondiaux (OMM-N° 558)
Cliquez sur l'image du livre à gauche. Les buts du Manuel sont les suivants: a) Préciser les obligations des Membres quant à la mise en oeuvre de l’assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes; b) Faciliter la coopération en matière de coordination internationale de l’assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes, en particulier la prestation du Service mondial OMI/OMM d’information et d’alerte pour la météorologie maritime et l’océanographie; c) Faciliter la coopération entre la Veille météorologique mondiale et l’assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes; d) Assurer l’uniformité des pratiques et des procédures employées pour atteindre les buts a), b) et c) ci‑dessus. Également disponible sur JCOMM.
- Manual de Servicios Meteorológicos Marinos - Aspectos mundiales (OMM-N° 558)
Haga clic en la imagen del libro a la izquierda. El presente Manual tiene por objeto: a) determinar las obligaciones de los Miembros en lo que respecta a la ejecución de los servicios meteorológicos marinos; b) facilitar la cooperación en materia de coordinación internacional de los servicios meteorológicos marinos, en concreto el suministro del Servicio mundial de información y avisos meteorológicos y oceanográficos de la Organización Marítima Internacional (OMI) y la Organización Meteorológica Mundial (OMM); c) facilitar la cooperación entre la Vigilancia Meteorológica Mundial y los servicios meteorológicos marinos; d) velar adecuadamente por la uniformidad y la normalización de las prácticas y los procedimientos empleados para conseguir los objetivos enunciados en a), b) y c). También disponible en JCOMM y DIRECTEMAR.
- Наставление по морскому метеорологическому обслуживанию - Глобальные аспекты (BMO-№ 558)
Нажмите на изображение книги слева. Настоящее Наставление предназначается: a) для определения обязанностей Членов в осуществлении морского метеорологического обслуживания (ММО); b) для облегчения сотрудничества в отношении международной координации ММО, в частности в осуществлении деятельности Всемирной службы Международной морской организации (ИМО)/ВМО метеорологической и океанографической информации и предупреждений (ВСМОИП); c) для облегчения сотрудничества между Всемирной службой погоды (ВСП) и ММО; d) для обеспечения надлежащей однородности и стандартизации практик и процедур, используемых для выполнения положений, упомянутых в подпунктах «a», «b» и «c» выше. Также доступно на JCOMM.
- Guide to Marine Meteorological Services (WMO-No. 471)

Internationally agreed methods of providing services to the marine community around the world are described in the Manual on Marine Meteorological Services (WMO-No. 558). The purpose of this Guide is to complement the Manual by: (a) Describing the requirements for the various types of service; (b) Explaining the rationale for the agreed methods of providing services; (c) Giving guidance on how to set up and maintain marine meteorological services. It follows the same structure as the Manual on Marine Meteorological Services. Also available on JCOMM. - Guide de l'assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes (OMM-N° 471)
Cliquez sur l'image du livre à gauche. C'est dans le Manuel de l'assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes (OMM N° 558) que sont décrites les méthodes reconnues en la matière sur le plan international. Dans le présent guide, qui constitue le complément de ce manuel, on s'attache à: a) Décrire les besoins correspondant aux diverses formes d'assistance; b) Justifier l'emploi des méthodes d'assistance retenues; c) Indiquer comment mettre en oeuvre et perpétuer l'assistance météorologique aux activités maritimes. Le Guide suit le même plan que le Manuel. Également disponible sur JCOMM.
- Guía de servicios meteorológicos marinos (OMM-N° 471)
Haga clic en la imagen del libro a la izquierda. En el Manual de servicios meteorológicos marinos (OMM N° 558) se describen los métodos convenidos internacionalmente para la prestación de servicios a la comunidad marina en todo el mundo. Como complemento de dicho Manual, la presente Guía responde a los siguientes propósitos: a) describir las necesidades requeridas para los distintos tipos de servicios; b) explicar las razones a que responden los métodos convenidos para la prestación de servicios; c) orientar sobre la manera de constituir y mantener servicios meteorológicos marinos. Para ello, está estructurada a semejanza del Manual de servicios meteorológicos marinos. También disponible en JCOMM y DIRECTEMAR.
- Руководство по морскому метеорологическому обслуживанию (BMO-№ 471)
Нажмите на изображение книги слева. Согласованные на международном уровне методы предоставления обслуживания морскому сообществу по всему миру описаны в Наставлении по морскому метеорологическому обслуживанию (ВМО-№ 558). Целью настоящего Руководства является дополнить Наставление посредством: a) описания требований к различным видам обслуживания; b) разъяснения целесообразности согласованных методов предоставления обслуживания; c) предоставления руководящих указаний в отношении того, каким образом следует организовывать и поддерживать морское метеорологическое обслуживание. Руководство имеет ту же структуру, что и Наставление по морскому метеорологическому обслуживанию. Также доступно на JCOMM.
- International Cloud Atlas - Web edition (WMO-No. 407)
Manual on the Observation of Clouds and Other Meteors. This on-line Atlas describes the classification system for clouds and meteorological phenomena used by all WMO Members. The classifications also describe meteorological meteors other than clouds – hydrometeors, lithometeors, photometeors, and electrometeors. The Atlas provides a common language to communicate cloud observations, and ensures consistency in reporting by observers around the world. It serves as a training tool for meteorologists, as well as for those working in aeronautical and maritime environments, and it has become popular with weather enthusiasts and cloud spotters.

- Atlas international des nuages - Édition web (OMM-N° 407)
Manuel de l'observation des nuages et des autres météores. Cet Atlas en ligne décrit le système de classification des nuages et des phénomènes météorologiques utilisé par tous les Membres de l'OMM. Les classifications traitent également des météores autres que les nuages – les hydrométéores, les lithométéores, les photométéores et les électrométéores. L'Atlas fournit une langue commune qui permet d'échanger des observations de nuages et assure la cohérence des informations fournies par les observateurs du monde entier. Il sert d'outil de formation pour les météorologues et les personnes qui travaillent dans les secteurs aéronautiques et maritimes. Il jouit d'une grande popularité auprès des passionnés et des observateurs de nuages amateurs.
- Atlas Internacional de Nubes - Edición web (OMM-N° 407)
Manual de observación de nubes y otros meteoros. En este Atlas se describe el sistema de clasificación de las nubes y los fenómenos meteorológicos que utilizan todos los Miembros de la OMM. Este sistema también describe los meteoros meteorológicos distintos de las nubes, a saber, los hidrometeoros, los hidrometeoros, los litometeoros, los fotometeoros y los electrometeoros. El Atlas ofrece un lenguaje común para comunicar las observaciones de las nubes y garantiza la coherencia en los informes de los observadores de todo el mundo. Sirve como herramienta de formación importante para los meteorólogos, así como para los que trabajan en entornos aeronáuticos y marinos, y se ha popularizado entre los aficionados a la meteorología y los observadores de las nubes.
- International Cloud Atlas - Volume II (WMO-No. 407, 1987)
Volume II of the International Cloud Atlas contains 196 pages of photographs, 161 of which are in colour, accompanied by concise yet detailed captions.
- International Cloud Atlas - Volume I (WMO-No. 407, 1975)
Manual on the observation of clouds and other meteors. Volume I of the International Cloud Atlas contains a descriptive and explanatory text concerning the general classification of meteors, clouds and meteors other than clouds.
- Manual on Codes (WMO-No. 306)
Volume I of the Manual on codes contains WMO international codes for meteorological data and other geophysical data relating to meteorology. It is issued in three volumes: Volume I.1 containing Part A (Alphanumeric Codes); Volume I.2 containing Part B (Binary Codes) and Part C (Common Features to Binary and Alphanumeric Codes); and Volume I.3 containing Part D (Representations derived from data models). Volume II contains, for the six WMO Regions and the Antarctic, the procedures for the use of international code forms as well as regional code forms and national coding practices, including national code forms.
- Manual on Codes, Volume I.1 – International Codes (WMO-No. 306): Part A – Alphanumeric Codes
- Manual on Codes, Volume I.2 – International Codes (WMO-No. 306): Part B – Binary Codes, Part C – Common Features to Binary and Alphanumeric Codes
- Manual on Codes, Volume I.3 – International Codes (WMO-No. 306): Part D – Representations derived from data models
- Manual on Codes, Volume II – Regional Codes and National Coding Practices (WMO-No. 306)
- Manuel des codes - Volume I.2

Le Volume I du Manuel des codes contient les codes internationaux de l’OMM pour l’échange des données météorologiques et d’autres données géophysiques se rapportant à la météorologie. Il est publié en trois volumes : le Volume I.1 contient la Partie A (Codes alphanumériques); le Volume I.2 contient la Partie B (Codes binaires) et la Partie C (Éléments communs aux codes binaires et alphanumérique); et le Volume I.3 contient la Partie D (Représentations dérivées de modèles de donnée). - GRIB - Manuals and guides
GRIB is a file format for the storage and transport of gridded meteorological data, such as Numerical Weather Prediction model output. It is designed to be self-describing, compact and portable across computer architectures. The GRIB standard was designed and is maintained by the World Meteorological Organization. Also legacy site.
- GRIB Edition 3 (FM 92-16)
- GRIB edition 1 (FM 92–XI)
- Introduction to GRIB Edition 1 and GRIB Edition 2 (legacy site)
- Guide to WMO Binary Code Form GRIB 1 (legacy site)
- Guide to FM92 GRIB edition 2 (legacy site)
- Latest Version of the Machine Readable Codes (Manual on Code, Volume I.2, WMO-No. 306)
- Sea-Ice Information Services in the World (WMO-No. 574)
The Sea Ice Information Services in the World is intended to provide to mariners and other users information on best practices in sea ice services available world-wide. The publication consists of two parts: Part I - A general description of the nature of sea ice, methods of observation, and the basis of ice-information services; Part II - A listing of the sea-ice information services available from 20 nations, given regionally. These details are supported by annexes containing sample charts and illustrating a wide selection of the products mentioned in Part II.
- Sea-Ice Nomenclature (WMO-No. 259)
This document provides snapshot of the WMO Sea Ice Nomenclature (WMO-No. 259, 2014) and includes 3 volumes: Volume I - Terminology and Codes (Linguistic equivalents in English, French, Russian and Spanish with 220 terms and definitions); Volume II - Illustrated Glossary (Contains 179 photos with ice terms arranged by subject) and Volume III - International System of Sea-Ice Symbols (Intended for use on synoptic and prognostic ice charts). Also:
- Electronic version of the Sea-Ice nomenclature: Predefined English, French, Russian and Spanish versions in alphabetic/subject order, equivalents, search/selection option (AARI)
- Sea Ice Nomenclature - Linguistic equivalents (WMO-No. 259, Suppl. No. 5): Nomenclature in English, French, Russian and Spanish (2009)
- Ice Chart Colour Code Standard (WMO/TD-No. 1215)
This document (JCOMM-TR-024) describes two separate colour codes for use on ice charts: the first one based on total concentration (CT) intended for use when the stage of development is relatively uniform but concentration is highly variable (e.g. arctic summer navigation) and the second one based on stage of development (SoD) intended for use when the concentration is relatively uniform (high) but the stage of development is variable (e.g. arctic winter navigation). Document is an integral part and extension of the WMO Sea Ice Nomenclature (WMO-No. 259) currently in force. Also 2004 version.
- Reference tables for international and Russian national symbology: Ice symbols in oval shapes and ice maps - JCOMM, 2005
- Справочные таблицы по элементам ледовой символики в овальной фигуре и ледовой карте - JCOMM, 2005
- Ice Logistics Portal - Ice charts (JCOMM)
The Ice Logistics Portal was created as a joint initiative of the International Ice Charting Working Group, the JCOMM Expert Team on Sea Ice and Polar View for the International Polar Year. It is now maintained by the German Bundesamt für Seeschifffahrt und Hydrographie. It is intended to create a convenient point of access to operational sea ice information produced by the world's ice services. Access to products is provided via a series of pre-defined regions for both the Arctic and the Antarctic. Since the primary focus of the Ice Logistics Portal is on operational sea ice data (i.e. ice charts), only the most recent information is displayed for any given region.
- SIGRID-3: A Vector Archive Format For Sea Ice Georeferenced Information And Data (WMO/TD-No. 1214)
This document (JCOMM-TR-023) describes Version 3.0 of SIGRID-3 (Sea Ice GeoReferenced Information and Data), an evolution of the SIGRID series of standards for coding, exchange and archiving of digital ice charts. Version 3.0 retains the essential structure of its predecessor and is backwards compatible with earlier versions of SIGRID-3. The important extension of Version 3 is to incorporate the features, attributes and encoding of the Ice Objects Catalogue for Electronic Navigation Charts (ENCs). The purpose of this extension is to facilitate the automatic translation of digital ice charts into S-57 and S-10x ENC formats.
- Electronic Chart Systems Ice Objects Catalogue (JCOMM-TR-080)
Electronic Navigation Charts (ENC) and Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS) are becoming widely available on ships navigating in icy waters and it is necessary to provide ice data in a form that can be used in these systems. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) established an on-line “registry” of ENC chart features. This registry contains several thematic “registers”, one of which is for ice objects. The information in the register derives directly from the ENC Ice Objects Catalogue. The Catlogue describes the ice objects and attributes equivalent to codes of SIGRID-3 transport format for the ice charts and defines what ice information can be used in IHO S-57 and S-411 formats.
- S411 ice charts for ECDIS (JCOMM)
The sea ice charts in S411 format are intended for the use in an ECDIS (or another GIS). The S-411 is fully based on the IHO S-100 framework specification, Geography Markup Language (GML), Encoding Standard and the ISO 19100 series of standards. It is a vector product specification that is primarily intended for encoding the extent and nature of Sea Ice for navigational purpose. Available actual ice charts are: Canadian East Coast - Canadian Eastern Arctic - Canadian Western Arctic - Hudson Bay - Great Lakes (From CIS). Alaska Waters (From US NWS). Greenland - NorthWest-Greenland - CentralWest-Greenland - CentralEast-Greenland - SouthEast-Greenland - Cape Farewell (From DMI). Northern North-Atlantic (From Met.no).
- WMO-IOC JCOMM Sea-Ice Regulatory Documents
Document list contains acting versions of the WMO-IOC JCOMM regulatory material related to sea-ice terminology, ice navigation and safety services, products exchange and presentation including ENC/ECDIS.
- ЛЕДОВЫЕ УСЛОВИЯ ПЛАВАНИЯ В ЮЖНОМ ОКЕАНЕ (ВМО/ТД-№ 783, 1996)
Режимно-справочное пособие для целей плавания, организации и осуществления судоходства в антарктических водах и льдах. Изложены природные особенности формирования ледового режима Южного океана и условий судоходства. Дана характеристика морских антарктических льдов и айсбергов, сформулированы основные закономерности их пространственно-временной изменчивости. Оценено влияние ледяного покрова на движение судов во льдах. Рекомендованы оптимальные маршруты и сроки плавания экспедиционных судов к антарктическим станциям, описаны ледово-навигационные условия судоходства. Изложены приемы и методы учета ледовых условий при выполнении грузовых операций у антарктического побережья. Рассмотрена современ-ная практика ледово-информационного обеспечения судоходства. Рекомендуется как режимно-справочное пособие для целейплавания, организации и осуществления судоходства в антарктических водах и льдах.
- WMO-IOC JCOMM Sea-Ice Regulatory Documents
Document list contains acting versions of the WMO-IOC JCOMM regulatory material related to sea-ice terminology, ice navigation and safety services, products exchange and presentation including ENC/ECDIS.
- Guide to Wave Analysis and Forecasting (WMO-No. 702, 2018)
- Severe Weather Information Centre
A centralized web site for severe weather around the world. This is a World Meteorological Organization (WMO) web site that provides a single and centralized source for tropical cyclones, heavy rain, gale, fog and thunderstorms. For example whenever a tropical cyclone develops, a tropical cyclone symbol will show up on the front page of this website with both position and strength indications. Furthermore, users can make use of the links provided in this website to find more information about these tropical cyclones such as forecast tracks and warnings issued.
- GMGSS / Limits of METAREAS - Marine weather services

| | COM |





L'urgence prime la forme - By Cr - 2012-2024
For updates, corrections, new charts or new documents please send an e-mail to
For my father and my mother / Pour mon père et ma mère

